Java 多线程:彻底搞懂线程池_java线程池-程序员宅基地
熟悉 Java 多线程编程的同学都知道,当我们线程创建过多时,容易引发内存溢出,因此我们就有必要使用线程池的技术了。
目录
5.2 定时线程池(ScheduledThreadPool )
5.4 单线程化线程池(SingleThreadExecutor)
1 线程池的优势
总体来说,线程池有如下的优势:
(1)降低资源消耗。通过重复利用已创建的线程降低线程创建和销毁造成的消耗。
(2)提高响应速度。当任务到达时,任务可以不需要等到线程创建就能立即执行。
(3)提高线程的可管理性。线程是稀缺资源,如果无限制的创建,不仅会消耗系统资源,还会降低系统的稳定性,使用线程池可以进行统一的分配,调优和监控。
2 线程池的使用
线程池的真正实现类是 ThreadPoolExecutor,其构造方法有如下4种:
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), defaultHandler);
}
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
threadFactory, defaultHandler);
}
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), handler);
}
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
if (corePoolSize < 0 ||
maximumPoolSize <= 0 ||
maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize ||
keepAliveTime < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize;
this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize;
this.workQueue = workQueue;
this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime);
this.threadFactory = threadFactory;
this.handler = handler;
}可以看到,其需要如下几个参数:
- corePoolSize(必需):核心线程数。默认情况下,核心线程会一直存活,但是当将 allowCoreThreadTimeout 设置为 true 时,核心线程也会超时回收。
- maximumPoolSize(必需):线程池所能容纳的最大线程数。当活跃线程数达到该数值后,后续的新任务将会阻塞。
- keepAliveTime(必需):线程闲置超时时长。如果超过该时长,非核心线程就会被回收。如果将 allowCoreThreadTimeout 设置为 true 时,核心线程也会超时回收。
- unit(必需):指定 keepAliveTime 参数的时间单位。常用的有:TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS(毫秒)、TimeUnit.SECONDS(秒)、TimeUnit.MINUTES(分)。
- workQueue(必需):任务队列。通过线程池的 execute() 方法提交的 Runnable 对象将存储在该参数中。其采用阻塞队列实现。
- threadFactory(可选):线程工厂。用于指定为线程池创建新线程的方式。
- handler(可选):拒绝策略。当达到最大线程数时需要执行的饱和策略。
线程池的使用流程如下:
// 创建线程池
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(CORE_POOL_SIZE,
MAXIMUM_POOL_SIZE,
KEEP_ALIVE,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
sPoolWorkQueue,
sThreadFactory);
// 向线程池提交任务
threadPool.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
... // 线程执行的任务
}
});
// 关闭线程池
threadPool.shutdown(); // 设置线程池的状态为SHUTDOWN,然后中断所有没有正在执行任务的线程
threadPool.shutdownNow(); // 设置线程池的状态为 STOP,然后尝试停止所有的正在执行或暂停任务的线程,并返回等待执行任务的列表3 线程池的工作原理
下面来描述一下线程池工作的原理,同时对上面的参数有一个更深的了解。其工作原理流程图如下:
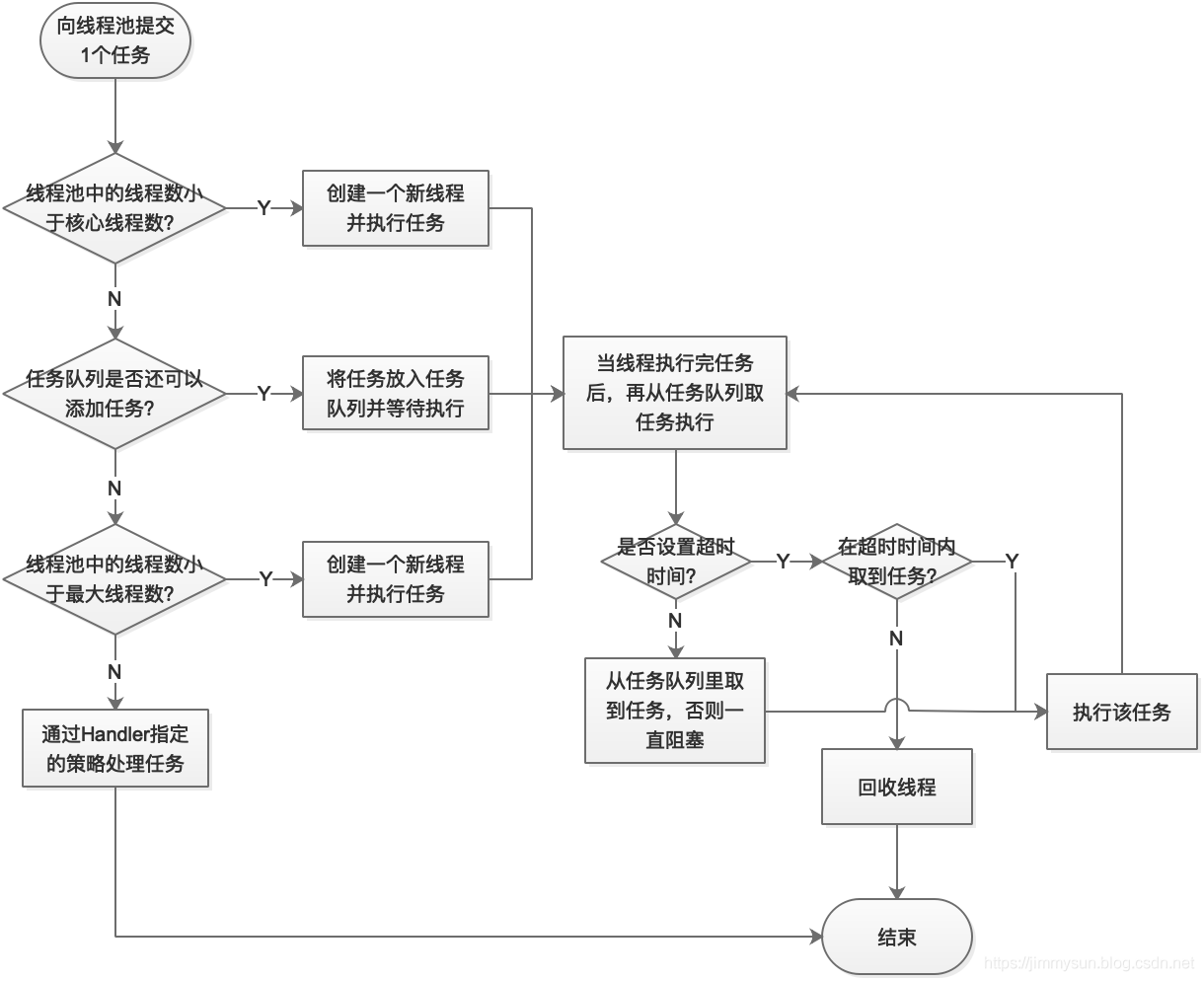
通过上图,相信大家已经对所有参数有个了解了。下面再对任务队列、线程工厂和拒绝策略做更多的说明。
4 线程池的参数
4.1 任务队列(workQueue)
任务队列是基于阻塞队列实现的,即采用生产者消费者模式,在 Java 中需要实现 BlockingQueue 接口。但 Java 已经为我们提供了 7 种阻塞队列的实现:
- ArrayBlockingQueue:一个由数组结构组成的有界阻塞队列(数组结构可配合指针实现一个环形队列)。
- LinkedBlockingQueue: 一个由链表结构组成的有界阻塞队列,在未指明容量时,容量默认为 Integer.MAX_VALUE。
- PriorityBlockingQueue: 一个支持优先级排序的无界阻塞队列,对元素没有要求,可以实现 Comparable 接口也可以提供 Comparator 来对队列中的元素进行比较。跟时间没有任何关系,仅仅是按照优先级取任务。
- DelayQueue:类似于PriorityBlockingQueue,是二叉堆实现的无界优先级阻塞队列。要求元素都实现 Delayed 接口,通过执行时延从队列中提取任务,时间没到任务取不出来。
- SynchronousQueue: 一个不存储元素的阻塞队列,消费者线程调用 take() 方法的时候就会发生阻塞,直到有一个生产者线程生产了一个元素,消费者线程就可以拿到这个元素并返回;生产者线程调用 put() 方法的时候也会发生阻塞,直到有一个消费者线程消费了一个元素,生产者才会返回。
- LinkedBlockingDeque: 使用双向队列实现的有界双端阻塞队列。双端意味着可以像普通队列一样 FIFO(先进先出),也可以像栈一样 FILO(先进后出)。
- LinkedTransferQueue: 它是ConcurrentLinkedQueue、LinkedBlockingQueue 和 SynchronousQueue 的结合体,但是把它用在 ThreadPoolExecutor 中,和 LinkedBlockingQueue 行为一致,但是是无界的阻塞队列。
注意有界队列和无界队列的区别:如果使用有界队列,当队列饱和时并超过最大线程数时就会执行拒绝策略;而如果使用无界队列,因为任务队列永远都可以添加任务,所以设置 maximumPoolSize 没有任何意义。
4.2 线程工厂(threadFactory)
线程工厂指定创建线程的方式,需要实现 ThreadFactory 接口,并实现 newThread(Runnable r) 方法。该参数可以不用指定,Executors 框架已经为我们实现了一个默认的线程工厂:
/**
* The default thread factory.
*/
private static class DefaultThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {
private static final AtomicInteger poolNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
private final ThreadGroup group;
private final AtomicInteger threadNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
private final String namePrefix;
DefaultThreadFactory() {
SecurityManager s = System.getSecurityManager();
group = (s != null) ? s.getThreadGroup() :
Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();
namePrefix = "pool-" +
poolNumber.getAndIncrement() +
"-thread-";
}
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread t = new Thread(group, r,
namePrefix + threadNumber.getAndIncrement(),
0);
if (t.isDaemon())
t.setDaemon(false);
if (t.getPriority() != Thread.NORM_PRIORITY)
t.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);
return t;
}
}4.3 拒绝策略(handler)
当线程池的线程数达到最大线程数时,需要执行拒绝策略。拒绝策略需要实现 RejectedExecutionHandler 接口,并实现 rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) 方法。不过 Executors 框架已经为我们实现了 4 种拒绝策略:
- AbortPolicy(默认):丢弃任务并抛出 RejectedExecutionException 异常。
- CallerRunsPolicy:由调用线程处理该任务。
- DiscardPolicy:丢弃任务,但是不抛出异常。可以配合这种模式进行自定义的处理方式。
- DiscardOldestPolicy:丢弃队列最早的未处理任务,然后重新尝试执行任务。
5 功能线程池
嫌上面使用线程池的方法太麻烦?其实Executors已经为我们封装好了 4 种常见的功能线程池,如下:
- 定长线程池(FixedThreadPool)
- 定时线程池(ScheduledThreadPool )
- 可缓存线程池(CachedThreadPool)
- 单线程化线程池(SingleThreadExecutor)
5.1 定长线程池(FixedThreadPool)
创建方法的源码:
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads, ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(),
threadFactory);
}- 特点:只有核心线程,线程数量固定,执行完立即回收,任务队列为链表结构的有界队列。
- 应用场景:控制线程最大并发数。
使用示例:
// 1. 创建定长线程池对象 & 设置线程池线程数量固定为3
ExecutorService fixedThreadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
// 2. 创建好Runnable类线程对象 & 需执行的任务
Runnable task =new Runnable(){
public void run() {
System.out.println("执行任务啦");
}
};
// 3. 向线程池提交任务
fixedThreadPool.execute(task);5.2 定时线程池(ScheduledThreadPool )
创建方法的源码:
private static final long DEFAULT_KEEPALIVE_MILLIS = 10L;
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) {
return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize);
}
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
DEFAULT_KEEPALIVE_MILLIS, MILLISECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue());
}
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(
int corePoolSize, ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize, threadFactory);
}
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
DEFAULT_KEEPALIVE_MILLIS, MILLISECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue(), threadFactory);
}- 特点:核心线程数量固定,非核心线程数量无限,执行完闲置 10ms 后回收,任务队列为延时阻塞队列。
- 应用场景:执行定时或周期性的任务。
使用示例:
// 1. 创建 定时线程池对象 & 设置线程池线程数量固定为5
ScheduledExecutorService scheduledThreadPool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5);
// 2. 创建好Runnable类线程对象 & 需执行的任务
Runnable task =new Runnable(){
public void run() {
System.out.println("执行任务啦");
}
};
// 3. 向线程池提交任务
scheduledThreadPool.schedule(task, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 延迟1s后执行任务
scheduledThreadPool.scheduleAtFixedRate(task,10,1000,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);// 延迟10ms后、每隔1000ms执行任务5.3 可缓存线程池(CachedThreadPool)
创建方法的源码:
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
}
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool(ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(),
threadFactory);
}- 特点:无核心线程,非核心线程数量无限,执行完闲置 60s 后回收,任务队列为不存储元素的阻塞队列。
- 应用场景:执行大量、耗时少的任务。
使用示例:
// 1. 创建可缓存线程池对象
ExecutorService cachedThreadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
// 2. 创建好Runnable类线程对象 & 需执行的任务
Runnable task =new Runnable(){
public void run() {
System.out.println("执行任务啦");
}
};
// 3. 向线程池提交任务
cachedThreadPool.execute(task);5.4 单线程化线程池(SingleThreadExecutor)
创建方法的源码:
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
}
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor(ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(),
threadFactory));
}- 特点:只有 1 个核心线程,无非核心线程,执行完立即回收,任务队列为链表结构的有界队列。
- 应用场景:不适合并发但可能引起 IO 阻塞性及影响 UI 线程响应的操作,如数据库操作、文件操作等。
使用示例:
// 1. 创建单线程化线程池
ExecutorService singleThreadExecutor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
// 2. 创建好Runnable类线程对象 & 需执行的任务
Runnable task =new Runnable(){
public void run() {
System.out.println("执行任务啦");
}
};
// 3. 向线程池提交任务
singleThreadExecutor.execute(task);5.5 对比
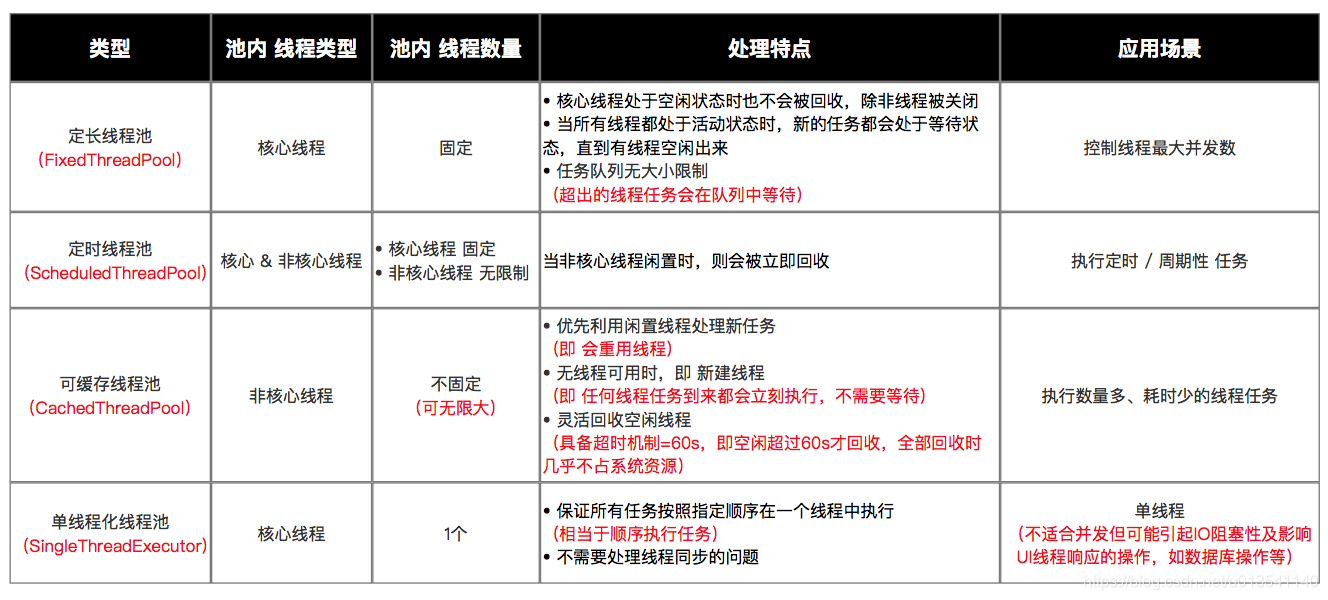
6 总结
Executors 的 4 个功能线程池虽然方便,但现在已经不建议使用了,而是建议直接通过使用 ThreadPoolExecutor 的方式,这样的处理方式让写的同学更加明确线程池的运行规则,规避资源耗尽的风险。
其实 Executors 的 4 个功能线程有如下弊端:
- FixedThreadPool 和 SingleThreadExecutor:主要问题是堆积的请求处理队列均采用 LinkedBlockingQueue,可能会耗费非常大的内存,甚至 OOM。
- CachedThreadPool 和 ScheduledThreadPool:主要问题是线程数最大数是 Integer.MAX_VALUE,可能会创建数量非常多的线程,甚至 OOM。
参考
智能推荐
linux里面ping www.baidu.com ping不通的问题_linux桥接ping不通baidu-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读3.2w次,点赞16次,收藏90次。对于这个问题我也是从网上找了很久,终于解决了这个问题。首先遇到这个问题,应该确认虚拟机能不能正常的上网,就需要ping 网关,如果能ping通说明能正常上网,不过首先要用命令route -n来查看自己的网关,如下图:第一行就是默认网关。现在用命令ping 192.168.1.1来看一下结果:然后可以看一下电脑上面百度的ip是多少可以在linux里面ping 这个IP,结果如下:..._linux桥接ping不通baidu
android 横幅弹出权限,有关 android studio notification 横幅弹出的功能没有反应-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读512次。小妹在这里已经卡了2-3天了,研究了很多人的文章,除了低版本api 17有成功外,其他的不是channel null 就是没反应 (channel null已解决)拜托各位大大,帮小妹一下,以下是我的程式跟 gradle, 我在这里卡好久又没有人可问(哭)public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivit..._android 权限申请弹窗 横屏
CNN中padding参数分类_cnn “相同填充”(same padding)-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1.4k次,点赞4次,收藏6次。valid padding(有效填充):完全不使用填充。half/same padding(半填充/相同填充):保证输入和输出的feature map尺寸相同。full padding(全填充):在卷积操作过程中,每个像素在每个方向上被访问的次数相同。arbitrary padding(任意填充):人为设定填充。..._cnn “相同填充”(same padding)
Maven的基础知识,java技术栈-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读790次,点赞29次,收藏28次。手绘了下图所示的kafka知识大纲流程图(xmind文件不能上传,导出图片展现),但都可提供源文件给每位爱学习的朋友一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远。不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎扫码加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长![外链图片转存中…(img-Qpoc4gOu-1712656009273)][外链图片转存中…(img-bSWbNeGN-1712656009274)]
getFullYear()和getYear()有什么区别_getyear和getfullyear-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读469次。Date对象取得年份有getYear和getFullYear两种方法经 测试var d=new Date;alert(d.getYear())在IE中返回 2009,在Firefox中会返回109。经查询手册,getYear在Firefox下返回的是距1900年1月1日的年份,这是一个过时而不被推荐的方法。而alert(d.getFullYear())在IE和FF中都会返回2009。因此,无论何时都应使用getFullYear来替代getYear方法。例如:2016年用 getFullYea_getyear和getfullyear
Unix传奇 (上篇)_unix传奇pdf-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读182次。Unix传奇(上篇) 陈皓 了解过去,我们才能知其然,更知所以然。总结过去,我们才会知道我们明天该如何去规划,该如何去走。在时间的滚轮中,许许多的东西就像流星一样一闪而逝,而有些东西却能经受着时间的考验散发着经久的魅力,让人津津乐道,流传至今。要知道明天怎么去选择,怎么去做,不是盲目地跟从今天各种各样琳琅满目前沿技术,而应该是去 —— 认认真真地了解和回顾历史。 Unix是目前还在存活的操作系_unix传奇pdf
随便推点
ACwing 哈希算法入门:_ac算法 哈希-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读308次。哈希算法:将字符串映射为数字形式,十分巧妙,一般运用为进制数,进制据前人经验,一般为131,1331时重复率很低,由于字符串的数字和会很大,所以一般为了方便,一般定义为unsigned long long,爆掉时,即为对 2^64 取模,可以对于任意子序列的值进行映射为数字进而进行判断入门题目链接:AC代码:#include<bits/stdc++.h>using na..._ac算法 哈希
VS配置Qt和MySQL_在vs中 如何装qt5sqlmysql模块-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读952次,点赞13次,收藏27次。由于觉得Qt的编辑界面比较丑,所以想用vs2022的编辑器写Qt加MySQL的项目。_在vs中 如何装qt5sqlmysql模块
【渝粤题库】广东开放大学 互联网营销 形成性考核_画中画广告之所以能有较高的点击率,主要由于它具有以下特点-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1k次。选择题题目:下面的哪个调研内容属于经济环境调研?()题目:()的目的就是加强与客户的沟通,它是是网络媒体也是网络营销的最重要特性。题目:4Ps策略中4P是指产品、价格、顾客和促销。题目:网络市场调研是目前最为先进的市场调研手段,没有任何的缺点或不足之处。题目:市场定位的基本参数有题目:市场需求调研可以掌握()等信息。题目:在开展企业网站建设时应做好以下哪几个工作。()题目:对企业网站首页的优化中,一定要注意下面哪几个方面的优化。()题目:()的主要作用是增进顾客关系,提供顾客服务,提升企业_画中画广告之所以能有较高的点击率,主要由于它具有以下特点
爬虫学习(1):urlopen库使用_urlopen the read operation timed out-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1k次,点赞2次,收藏5次。以爬取CSDN为例子:第一步:导入请求库第二步:打开请求网址第三步:打印源码import urllib.requestresponse=urllib.request.urlopen("https://www.csdn.net/?spm=1011.2124.3001.5359")print(response.read().decode('utf-8'))结果大概就是这个样子:好的,继续,看看打印的是什么类型的:import urllib.requestresponse=urllib.r_urlopen the read operation timed out
分享读取各大主流邮箱通讯录(联系人)、MSN好友列表的的功能【升级版(3.0)】-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读304次。修正sina.com/sina.cn邮箱获取不到联系人,并精简修改了其他邮箱代码,以下就是升级版版本的介绍:完整版本,整合了包括读取邮箱通讯录、MSN好友列表的的功能,目前读取邮箱通讯录支持如下邮箱:gmail(Y)、hotmail(Y)、 live(Y)、tom(Y)、yahoo(Y)(有点慢)、 sina(Y)、163(Y)、126(Y)、yeah(Y)、sohu(Y) 读取后可以发送邮件(完..._通讯录 应用读取 邮件 的相关
云计算及虚拟化教程_云计算与虚拟化技术 教改-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读213次。云计算及虚拟化教程学习云计算、虚拟化和计算机网络的基本概念。此视频教程共2.0小时,中英双语字幕,画质清晰无水印,源码附件全课程英文名:Cloud Computing and Virtualization An Introduction百度网盘地址:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1lrak60XOGEqMOI6lXYf6TQ?pwd=ns0j课程介绍:https://www.aihorizon.cn/72云计算:概念、定义、云类型和服务部署模型。虚拟化的概念使用 Type-2 Hyperv_云计算与虚拟化技术 教改