OpenCL的学习_opencl failed to load kernel of get_xw_xy.cl!-程序员宅基地
技术标签: Improve Performance OpenCL
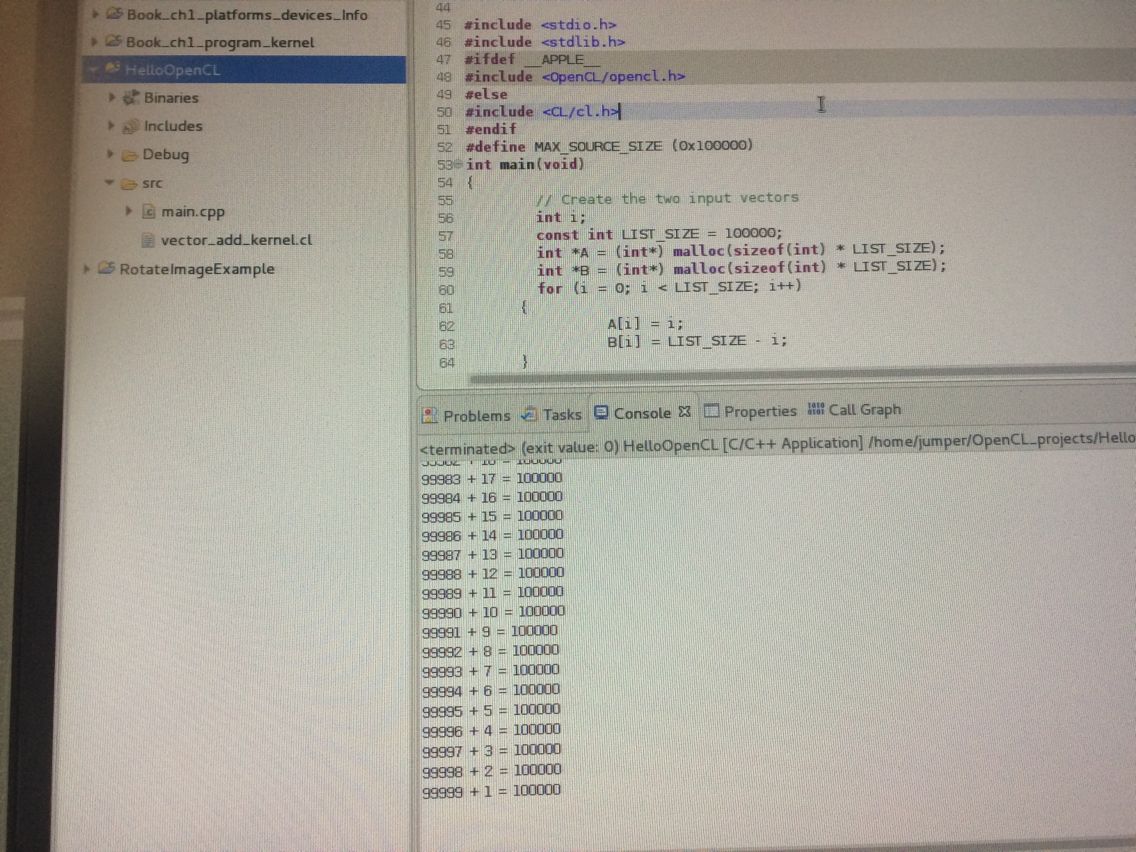
环境:CentOS7 显卡:NVIDIA 按照http://blog.csdn.net/fly_yr/article/details/49796649配置好OpenCL 然后按照:https://docs.google.com/document/pub?id=1NPo1TK30IOYZxI53t_V3uenSHTMSFYs5cupVDniqVK4 运行这个小例子测试是否配置好了 本来我一直报错说:failed to load kernel. 把代码中这一句fp = fopen("vector_add_kernel.cl", "r");改成绝对路径 比如我的是fp = fopen("/home/.../vector_add_kernel.cl", "r");即可 哦中间还报了一个小错误说头文件‘CL/cl.h’没有这个目录或头文件 解决办法:yum install opencl-headers就不报错了。 出来是两个非负整数相加等于1000的所有可能。
1、我是先对着上面那个程序 然后看这个博客 http://blog.csdn.net/leonwei/article/category/1410041 初步了解OpenCL
2、对着http://blog.csdn.net/lien0906/article/category/2925315 http://blog.csdn.net/Augusdi/article/category/1687179 进一步熟悉 OpenCV的OCL模块就是支持OpenCL的哦 如果只是用OpenCL进行图像开发 就用这个应该就够了吧 但目前好像上面包含的函数比较少哎 相同部分可跳过
3、对着http://www.cnblogs.com/mikewolf2002/category/343145.html 学习
4、上面都看完后 按照http://www.cnblogs.com/mikewolf2002/archive/2012/09/11/2680689.html 这位大神的OpenCL系列 有很多篇。我看到图像旋转这里:
这之前几篇还有一个向量相加的小程序:因为我是linux 改了点:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#ifdef __APPLE__
#include <OpenCL/opencl.h>
#else
#include <CL/cl.h>
#endif
#define MAX_SOURCE_SIZE (0x100000)
int main(void)
{
// Create the two input vectors
int i;
const int LIST_SIZE = 100000;
int *A = (int*) malloc(sizeof(int) * LIST_SIZE);
int *B = (int*) malloc(sizeof(int) * LIST_SIZE);
for (i = 0; i < LIST_SIZE; i++)
{
A[i] = i;
B[i] = LIST_SIZE - i;
}
/// Load the kernel source code into the array source_str
FILE *fp;
char *source_str;
size_t source_size;
fp = fopen("/home/jumper/OpenCL_projects/HelloOpenCL/src/vector_add_kernel.cl", "r");
if (!fp)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to load kernel.\n");
exit(1);
}
source_str = (char*) malloc(MAX_SOURCE_SIZE);
source_size = fread(source_str, 1, MAX_SOURCE_SIZE, fp);
fclose(fp);
/ Get platform and device information
cl_platform_id platform_id = NULL;
cl_device_id device_id = NULL;
cl_uint ret_num_devices;
cl_uint ret_num_platforms;
cl_int ret = clGetPlatformIDs(1, &platform_id, &ret_num_platforms);
ret = clGetDeviceIDs(platform_id, CL_DEVICE_TYPE_DEFAULT, 1, &device_id,
&ret_num_devices);
/ Create an OpenCL context
cl_context context = clCreateContext(NULL, 1, &device_id, NULL, NULL, &ret);
/ Create a command queue
cl_command_queue command_queue = clCreateCommandQueue(context, device_id, 0,
&ret);
/ Create memory buffers on the device for each vector
cl_mem a_mem_obj = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_READ_ONLY,
LIST_SIZE * sizeof(int), NULL, &ret);
cl_mem b_mem_obj = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_READ_ONLY,
LIST_SIZE * sizeof(int), NULL, &ret);
cl_mem c_mem_obj = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_WRITE_ONLY,
LIST_SIZE * sizeof(int), NULL, &ret);
// Copy the lists A and B to their respective memory buffers
ret = clEnqueueWriteBuffer(command_queue, a_mem_obj, CL_TRUE, 0,
LIST_SIZE * sizeof(int), A, 0, NULL, NULL);
ret = clEnqueueWriteBuffer(command_queue, b_mem_obj, CL_TRUE, 0,
LIST_SIZE * sizeof(int), B, 0, NULL, NULL);
// Create a program from the kernel source
cl_program program = clCreateProgramWithSource(context, 1,
(const char **) &source_str, (const size_t *) &source_size, &ret);
// Build the program
ret = clBuildProgram(program, 1, &device_id, NULL, NULL, NULL);
// Create the OpenCL kernel
cl_kernel kernel = clCreateKernel(program, "vector_add", &ret);
// Set the arguments of the kernel
ret = clSetKernelArg(kernel, 0, sizeof(cl_mem), (void *) &a_mem_obj);
ret = clSetKernelArg(kernel, 1, sizeof(cl_mem), (void *) &b_mem_obj);
ret = clSetKernelArg(kernel, 2, sizeof(cl_mem), (void *) &c_mem_obj);
// Execute the OpenCL kernel on the list
size_t global_item_size = LIST_SIZE; // Process the entire lists
size_t local_item_size = 1; // Process one item at a time
ret = clEnqueueNDRangeKernel(command_queue, kernel, 1, NULL,
&global_item_size, &local_item_size, 0, NULL, NULL);
// Read the memory buffer C on the device to the local variable C
int *C = (int*) malloc(sizeof(int) * LIST_SIZE);
ret = clEnqueueReadBuffer(command_queue, c_mem_obj, CL_TRUE, 0,
LIST_SIZE * sizeof(int), C, 0, NULL, NULL);
// Display the result to the screen
for (i = 0; i < LIST_SIZE; i++)
printf("%d + %d = %d\n", A[i], B[i], C[i]);
// Clean up
ret = clFlush(command_queue);
ret = clFinish(command_queue);
ret = clReleaseKernel(kernel);
ret = clReleaseProgram(program);
ret = clReleaseMemObject(a_mem_obj);
ret = clReleaseMemObject(b_mem_obj);
ret = clReleaseMemObject(c_mem_obj);
ret = clReleaseCommandQueue(command_queue);
ret = clReleaseContext(context);
free(A);
free(B);
free(C);
return 0;
}结果:
再看这个图像旋转的:
#include <CL/cl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string.h>
#include "gclFile.h"
//#include "gclTimer.h"
#include "gFreeImage.h"
using namespace std;
int waitForEventAndRelease(cl_event *event)
{
cl_int status = CL_SUCCESS;
cl_int eventStatus = CL_QUEUED;
while(eventStatus != CL_COMPLETE)
{
status = clGetEventInfo(*event,CL_EVENT_COMMAND_EXECUTION_STATUS,sizeof(cl_int),&eventStatus,NULL);
}
//status = clReleaseEvent(*event); //it causes error:No source available "0*0"
return 0;
}
void cpu_rotate(unsigned char* inbuf, unsigned char* outbuf, int w, int h,float sinTheta, float cosTheta)
{
int i, j;
int xc = w/2;
int yc = h/2;
for(i = 0; i < h; i++)
{
for(j=0; j< w; j++)
{
int xpos = ( j-xc)*cosTheta - (i-yc)*sinTheta+xc;
int ypos = (j-xc)*sinTheta + ( i-yc)*cosTheta+yc;
if(xpos>=0&&ypos>=0&&xpos<w&&ypos<h)
outbuf[ypos*w + xpos] = inbuf[i*w+j];
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
//the first step :get image and image informations!
unsigned char *src_image=0;
unsigned char *cpu_image=0;
int W, H;
gFreeImage img;
int readflag=img.LoadImageGrey("/home/jumper/OpenCL_projects/RotateImageExample/lenna.jpg");
if(!readflag)
{
printf("cannot load lenna.jpg\n");
exit(0);
}
else
src_image = img.getImageDataGrey(W, H);
size_t mem_size = W*H;
cpu_image = (unsigned char*)malloc(mem_size);
putenv("GPU_DUMP_DEVICE_KERNEL=3");
//the second step:get all devices which support OpenCL and decide which one to be used!
cl_uint status;
cl_platform_id platform;
cl_uint numPlatforms;
std::string platformVendor;
status = clGetPlatformIDs(0, NULL, &numPlatforms);
printf("Number of OpenCL platforms found:%d\n",numPlatforms);
if(status != CL_SUCCESS)
{
return 0;
}
if (0 < numPlatforms)
{
cl_platform_id* platforms = new cl_platform_id[numPlatforms];
status = clGetPlatformIDs(numPlatforms, platforms, NULL);
char platformName[100];
for (unsigned i = 0; i < numPlatforms; ++i)
{
status = clGetPlatformInfo(platforms[i],CL_PLATFORM_VENDOR,sizeof(platformName),platformName,NULL);
platform = platforms[i];
platformVendor.assign(platformName);
if (!strcmp(platformName, "Advanced Micro Devices, Inc."))
{
break;
}
}
std::cout << "Platform found : " << platformName << "\n";
delete[] platforms;
}
//Choose the best platform as the device to be used!
cl_device_id device;
clGetDeviceIDs( platform, CL_DEVICE_TYPE_GPU,1,&device,NULL);
//Create context and Commandqueue
cl_context context = clCreateContext( NULL,1,&device,NULL, NULL, NULL);
cl_command_queue queue = clCreateCommandQueue( context,device,CL_QUEUE_PROFILING_ENABLE, NULL );
//Create READ/WRITE Buffer to receive real arguments of kernel function!
cl_mem d_ip = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_READ_ONLY,mem_size, NULL, NULL);
cl_mem d_op = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_WRITE_ONLY,mem_size, NULL, NULL);
//for READ Buffer :Received real arguments from host
cl_event writeEvt;
status = clEnqueueWriteBuffer ( queue , d_ip, CL_TRUE,0, mem_size, (void *)src_image,0, NULL, &writeEvt);
status = clFlush(queue);
waitForEventAndRelease(&writeEvt);
cl_int relea = clReleaseEvent(writeEvt);
//load the kernel function and compile it!
gclFile kernelFile;
if(!kernelFile.open("/home/jumper/OpenCL_projects/RotateImageExample/rotate.cl"))
{
printf("Failed to load kernel file \n");
exit(0);
}
const char * source = kernelFile.source().c_str();
size_t sourceSize[] = {strlen(source)};
cl_program program = clCreateProgramWithSource(context, 1, &source,sourceSize,NULL);
status = clBuildProgram( program, 1, &device, NULL, NULL, NULL );
if(status != 0)
{
printf("clBuild failed:%d\n", status);
char tbuf[0x10000];
clGetProgramBuildInfo(program, device, CL_PROGRAM_BUILD_LOG, 0x10000, tbuf, NULL);
printf("\n%s\n", tbuf);
return -1;
}
//send the real arguments to the kernel functions!
cl_kernel kernel = clCreateKernel( program, "image_rotate", NULL );
float sintheta = 1, costheta = 0;
clSetKernelArg(kernel, 0, sizeof(cl_mem), (void *)&d_ip);
clSetKernelArg(kernel, 1, sizeof(cl_mem), (void *)&d_op);
clSetKernelArg(kernel, 2, sizeof(cl_int), (void *)&W);
clSetKernelArg(kernel, 3, sizeof(cl_int), (void *)&H);
clSetKernelArg(kernel, 4, sizeof(cl_float), (void *)&sintheta);
clSetKernelArg(kernel, 5, sizeof(cl_float), (void *)&costheta);
//Set the sizes of Work Item and Work group,then run the kernel!
cl_event ev;
size_t globalThreads[] = {W, H};
size_t localThreads[] = {16, 16};
printf("global_work_size =(%d,%d), local_work_size=(16, 16)\n",W,H);
clEnqueueNDRangeKernel( queue,kernel,2,NULL,globalThreads,localThreads, 0, NULL, &ev);
status = clFlush( queue );
waitForEventAndRelease(&ev);
cl_ulong startTime, endTime;
size_t ulong_size=sizeof(cl_ulong);
clGetEventProfilingInfo(ev, CL_PROFILING_COMMAND_START, sizeof(cl_ulong), &startTime, NULL);
clGetEventProfilingInfo(ev, CL_PROFILING_COMMAND_END,sizeof(cl_ulong), &endTime, NULL);
cl_ulong kernelExecTimeNs = endTime-startTime;
printf("kernal exec time :%8.6f ms\n ", kernelExecTimeNs*1e-6 );
cl_int releas=clReleaseEvent(ev);
//Copy results you need from device back to host!
unsigned char *op_data=0;
cl_event mapevt;
op_data = (cl_uchar *) clEnqueueMapBuffer( queue,d_op,CL_TRUE,CL_MAP_READ,0, mem_size,0, NULL, &mapevt, NULL );
status = clFlush( queue );
waitForEventAndRelease(&mapevt);
cl_int release3=clReleaseEvent(mapevt);
int i;
cpu_rotate(src_image,cpu_image, W, H, 1, 0);
for(i = 0; i < mem_size; i++)
{
src_image[i] =cpu_image[i];
}
img.SaveImage("/home/jumper/OpenCL_projects/RotateImageExample/cpu_lenna_rotate.jpg");
for(i = 0; i < mem_size; i++)
{
src_image[i] =op_data[i];
}
img.SaveImage("/home/jumper/OpenCL_projects/RotateImageExample/lenna_rotate.jpg");
if(cpu_image)
free(cpu_image);
//Release some arguments on device and host!
clReleaseMemObject(d_ip);
clReleaseMemObject(d_op);
clReleaseProgram(program);
clReleaseCommandQueue(queue);
clReleaseContext(context);
return 0;
}
5、后来发现这本书 《OpenCL Parallel Programming Development CookBook》就下载下来了 真的很好 而且提供了源代码 边运行代码边看书上的讲解 真的感觉不那么难了。 但我没全部照着运行 改动了的
6、《OpenCL Parallel Programming Development CookBook》-Ch1
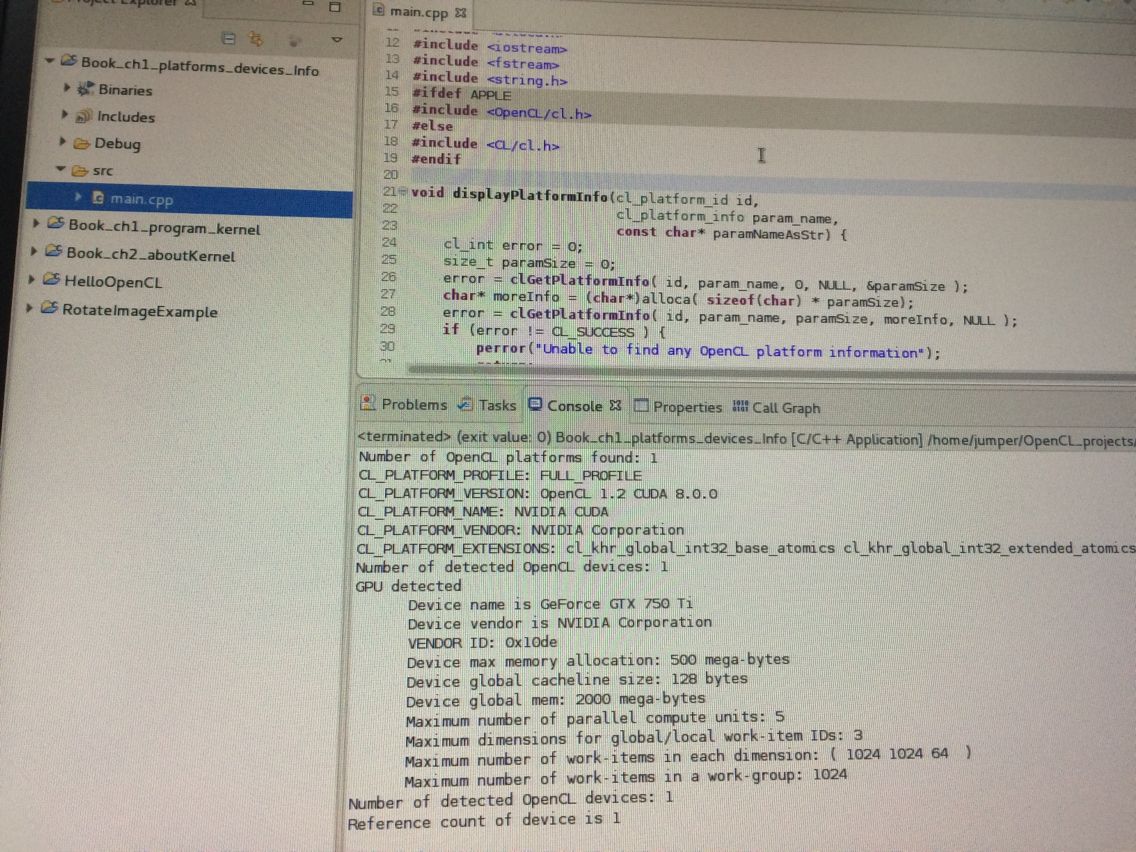
书上几个例子综合一下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <alloca.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string.h>
#ifdef APPLE
#include <OpenCL/cl.h>
#else
#include <CL/cl.h>
#endif
void displayPlatformInfo(cl_platform_id id,
cl_platform_info param_name,
const char* paramNameAsStr) {
cl_int error = 0;
size_t paramSize = 0;
error = clGetPlatformInfo( id, param_name, 0, NULL, ¶mSize );
char* moreInfo = (char*)alloca( sizeof(char) * paramSize);
error = clGetPlatformInfo( id, param_name, paramSize, moreInfo, NULL );
if (error != CL_SUCCESS ) {
perror("Unable to find any OpenCL platform information");
return;
}
printf("%s: %s\n", paramNameAsStr, moreInfo);
}
void displayDeviceDetails(cl_device_id id,
cl_device_info param_name,
const char* paramNameAsStr) {
cl_int error = 0;
size_t paramSize = 0;
error = clGetDeviceInfo( id, param_name, 0, NULL, ¶mSize );
if (error != CL_SUCCESS ) {
perror("Unable to obtain device info for param\n");
return;
}
/* the cl_device_info are preprocessor directives defined in cl.h */
switch (param_name) {
case CL_DEVICE_TYPE: {
cl_device_type* devType = (cl_device_type*) alloca(sizeof(cl_device_type) * paramSize);
error = clGetDeviceInfo( id, param_name, paramSize, devType, NULL );
if (error != CL_SUCCESS ) {
perror("Unable to obtain device info for param\n");
return;
}
switch (*devType) {
case CL_DEVICE_TYPE_CPU : printf("CPU detected\n");break;
case CL_DEVICE_TYPE_GPU : printf("GPU detected\n");break;
case CL_DEVICE_TYPE_ACCELERATOR : printf("Accelerator detected\n");break;
case CL_DEVICE_TYPE_DEFAULT : printf("default detected\n");break;
}
}break;
case CL_DEVICE_VENDOR_ID :
case CL_DEVICE_MAX_COMPUTE_UNITS :
case CL_DEVICE_MAX_WORK_ITEM_DIMENSIONS : {
cl_uint* ret = (cl_uint*) alloca(sizeof(cl_uint) * paramSize);
error = clGetDeviceInfo( id, param_name, paramSize, ret, NULL );
if (error != CL_SUCCESS ) {
perror("Unable to obtain device info for param\n");
return;
}
switch (param_name) {
case CL_DEVICE_VENDOR_ID: printf("\tVENDOR ID: 0x%x\n", *ret); break;
case CL_DEVICE_MAX_COMPUTE_UNITS: printf("\tMaximum number of parallel compute units: %d\n", *ret); break;
case CL_DEVICE_MAX_WORK_ITEM_DIMENSIONS: printf("\tMaximum dimensions for global/local work-item IDs: %d\n", *ret); break;
}
}break;
case CL_DEVICE_MAX_WORK_ITEM_SIZES : {
cl_uint maxWIDimensions;
size_t* ret = (size_t*) alloca(sizeof(size_t) * paramSize);
error = clGetDeviceInfo( id, param_name, paramSize, ret, NULL );
error = clGetDeviceInfo( id, CL_DEVICE_MAX_WORK_ITEM_DIMENSIONS, sizeof(cl_uint), &maxWIDimensions, NULL );
if (error != CL_SUCCESS ) {
perror("Unable to obtain device info for param\n");
return;
}
printf("\tMaximum number of work-items in each dimension: ( ");
for(cl_int i =0; i < maxWIDimensions; ++i ) {
printf("%d ", ret[i]);
}
printf(" )\n");
}break;
case CL_DEVICE_MAX_WORK_GROUP_SIZE : {
size_t* ret = (size_t*) alloca(sizeof(size_t) * paramSize);
error = clGetDeviceInfo( id, param_name, paramSize, ret, NULL );
if (error != CL_SUCCESS ) {
perror("Unable to obtain device info for param\n");
return;
}
printf("\tMaximum number of work-items in a work-group: %d\n", *ret);
}break;
case CL_DEVICE_NAME :
case CL_DEVICE_VENDOR : {
char data[48];
error = clGetDeviceInfo( id, param_name, paramSize, data, NULL );
if (error != CL_SUCCESS ) {
perror("Unable to obtain device name/vendor info for param\n");
return;
}
switch (param_name) {
case CL_DEVICE_NAME : printf("\tDevice name is %s\n", data);break;
case CL_DEVICE_VENDOR : printf("\tDevice vendor is %s\n", data);break;
}
} break;
case CL_DEVICE_GLOBAL_MEM_CACHELINE_SIZE: {
cl_uint* size = (cl_uint*) alloca(sizeof(cl_uint) * paramSize);
error = clGetDeviceInfo( id, param_name, paramSize, size, NULL );
if (error != CL_SUCCESS ) {
perror("Unable to obtain device name/vendor info for param\n");
return;
}
printf("\tDevice global cacheline size: %d bytes\n", (*size)); break;
} break;
case CL_DEVICE_GLOBAL_MEM_SIZE:
case CL_DEVICE_MAX_MEM_ALLOC_SIZE: {
cl_ulong* size = (cl_ulong*) alloca(sizeof(cl_ulong) * paramSize);
error = clGetDeviceInfo( id, param_name, paramSize, size, NULL );
if (error != CL_SUCCESS ) {
perror("Unable to obtain device name/vendor info for param\n");
return;
}
switch (param_name) {
case CL_DEVICE_GLOBAL_MEM_SIZE: printf("\tDevice global mem: %ld mega-bytes\n", (*size)>>20); break;
case CL_DEVICE_MAX_MEM_ALLOC_SIZE: printf("\tDevice max memory allocation: %ld mega-bytes\n", (*size)>>20); break;
}
} break;
} //end of switch
}
void displayDeviceInfo(cl_platform_id id,
cl_device_type dev_type) {
/* OpenCL 1.1 device types */
cl_int error = 0;
cl_uint numOfDevices = 0;
/* Determine how many devices are connected to your platform */
error = clGetDeviceIDs(id, dev_type, 0, NULL, &numOfDevices);
if (error != CL_SUCCESS ) {
perror("Unable to obtain any OpenCL compliant device info");
exit(1);
}
cl_device_id* devices = (cl_device_id*) alloca(sizeof(cl_device_id) * numOfDevices);
/* Load the information about your devices into the variable 'devices' */
error = clGetDeviceIDs(id, dev_type, numOfDevices, devices, NULL);
if (error != CL_SUCCESS ) {
perror("Unable to obtain any OpenCL compliant device info");
exit(1);
}
printf("Number of detected OpenCL devices: %d\n", numOfDevices);
/* We attempt to retrieve some information about the devices. */
for(int i = 0; i < numOfDevices; ++ i ) {
displayDeviceDetails( devices[i], CL_DEVICE_TYPE, "CL_DEVICE_TYPE" );
displayDeviceDetails( devices[i], CL_DEVICE_NAME, "CL_DEVICE_NAME" );
displayDeviceDetails( devices[i], CL_DEVICE_VENDOR, "CL_DEVICE_VENDOR" );
displayDeviceDetails( devices[i], CL_DEVICE_VENDOR_ID, "CL_DEVICE_VENDOR_ID" );
displayDeviceDetails( devices[i], CL_DEVICE_MAX_MEM_ALLOC_SIZE, "CL_DEVICE_MAX_MEM_ALLOC_SIZE" );
displayDeviceDetails( devices[i], CL_DEVICE_GLOBAL_MEM_CACHELINE_SIZE, "CL_DEVICE_GLOBAL_MEM_CACHELINE_SIZE" );
displayDeviceDetails( devices[i], CL_DEVICE_GLOBAL_MEM_SIZE, "CL_DEVICE_GLOBAL_MEM_SIZE" );
displayDeviceDetails( devices[i], CL_DEVICE_MAX_COMPUTE_UNITS, "CL_DEVICE_MAX_COMPUTE_UNITS" );
displayDeviceDetails( devices[i], CL_DEVICE_MAX_WORK_ITEM_DIMENSIONS, "CL_DEVICE_MAX_WORK_ITEM_DIMENSIONS" );
displayDeviceDetails( devices[i], CL_DEVICE_MAX_WORK_ITEM_SIZES, "CL_DEVICE_MAX_WORK_ITEM_SIZES" );
displayDeviceDetails( devices[i], CL_DEVICE_MAX_WORK_GROUP_SIZE, "CL_DEVICE_MAX_WORK_GROUP_SIZE" );
}
}
void createAndReleaseContext(cl_platform_id id,
cl_device_type dev_type) {
/* OpenCL 1.1 device types */
cl_int error = 0;
cl_uint numOfDevices = 0;
/* Determine how many devices are connected to your platform */
error = clGetDeviceIDs(id, dev_type, 0, NULL, &numOfDevices);
if (error != CL_SUCCESS ) {
perror("Unable to obtain any OpenCL compliant device info");
exit(1);
}
cl_device_id* devices = (cl_device_id*) alloca(sizeof(cl_device_id) * numOfDevices);
/* Load the information about your devices into the variable 'devices' */
error = clGetDeviceIDs(id, dev_type, numOfDevices, devices, NULL);
if (error != CL_SUCCESS ) {
perror("Unable to obtain any OpenCL compliant device info");
exit(1);
}
printf("Number of detected OpenCL devices: %d\n", numOfDevices);
/*
We attempt to create contexts for each device we find, report it
and release the context. Once a context is created, its context is implicitly
retained and so you don't have to invoke 'clRetainContext'
*/
for(int i = 0; i < numOfDevices; ++ i ) {
cl_context context = clCreateContext(NULL, 1, &devices[i], NULL, NULL, &error);
cl_uint ref_cnt = 0;
if (error != CL_SUCCESS) {
perror("Can't create a context");
exit(1);
}
error = clGetContextInfo(context, CL_CONTEXT_REFERENCE_COUNT, sizeof(ref_cnt), &ref_cnt, NULL);
if (error != CL_SUCCESS) {
perror("Can't obtain context information");
exit(1);
}
printf("Reference count of device is %d\n", ref_cnt);
// Release the context
clReleaseContext(context);
}
}
int main() {
//Get all the platforms that support OpenCL!
cl_platform_id* platforms;
cl_uint numOfPlatforms;
cl_int error;
error = clGetPlatformIDs(0, NULL, &numOfPlatforms);
if(error != CL_SUCCESS) {
perror("Unable to find any OpenCL platforms");
exit(1);
}
printf("Number of OpenCL platforms found: %d\n", numOfPlatforms);
//Get the addresses of every platform. Allocate memory for the number of installed platforms.
// alloca(...) occupies some stack space but is automatically freed on return
platforms = (cl_platform_id*) alloca(sizeof(cl_platform_id) * numOfPlatforms);
error = clGetPlatformIDs(numOfPlatforms, platforms, NULL);
if(error != CL_SUCCESS) {
perror("Unable to find any OpenCL platforms");
exit(1);
}
//visit every platform by their addresses.
for(cl_uint i = 0; i < numOfPlatforms; ++i) {
//platforms information
displayPlatformInfo( platforms[i], CL_PLATFORM_PROFILE, "CL_PLATFORM_PROFILE" );
displayPlatformInfo( platforms[i], CL_PLATFORM_VERSION, "CL_PLATFORM_VERSION" );
displayPlatformInfo( platforms[i], CL_PLATFORM_NAME, "CL_PLATFORM_NAME" );
displayPlatformInfo( platforms[i], CL_PLATFORM_VENDOR, "CL_PLATFORM_VENDOR" );
displayPlatformInfo( platforms[i], CL_PLATFORM_EXTENSIONS, "CL_PLATFORM_EXTENSIONS" );
//devices information
displayDeviceInfo( platforms[i], CL_DEVICE_TYPE_ALL );
//contexts information with devices
createAndReleaseContext( platforms[i], CL_DEVICE_TYPE_ALL );
}
return 0;
}
书上有句话解释了 不同的SDK对OpenCL platform和device的支持不一样 NVIDIA只支持GPU AMD公司的支持CPU和GPU 等
学完第一章,我试着写了个:
#include <iostream>
#include <CL/cl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "gclFile.h"
void loadProgramSource(const char** files,
size_t length,
char** buffer,
size_t* sizes) {
/* Read each source file (*.cl) and store the contents into a temporary datastore */
for(size_t i=0; i < length; i++) {
FILE* file = fopen(files[i], "r");
if(file == NULL) {
perror("Couldn't read the program file");
exit(1);
}
fseek(file, 0, SEEK_END);
sizes[i] = ftell(file);
rewind(file); // reset the file pointer so that 'fread' reads from the front
buffer[i] = (char*)malloc(sizes[i]+1);
buffer[i][sizes[i]] = '\0';
fread(buffer[i], sizeof(char), sizes[i], file);
fclose(file);
}
}
int main(){
//first : platform
cl_uint platformnum;
cl_int error;
error=clGetPlatformIDs(0,NULL,&platformnum);
if(error!=CL_SUCCESS){
printf("no suitable platforms for OpenCL\n");
return -1;
}
cl_platform_id* platformIDs;
platformIDs=(cl_platform_id*)alloca(sizeof(cl_platform_id)*platformnum);
error=clGetPlatformIDs(platformnum,platformIDs,NULL);
if(error!=CL_SUCCESS){
printf("platforms addresses error\n");
return -1;
}
//second:device
cl_device_id device;
char platformName[100];
error = clGetPlatformInfo(platformIDs[0],CL_PLATFORM_VENDOR,sizeof(platformName),platformName,NULL);
if(error!=CL_SUCCESS){
printf("wrong when getting the platform in use.\n");
return -1;
}
cl_platform_id platformInUse = platformIDs[0];
clGetDeviceIDs(platformInUse,CL_DEVICE_TYPE_GPU,1,&device,NULL);
//third: context and CommandQueue
cl_context context=clCreateContext(NULL,1,&device,NULL,NULL,NULL);
cl_command_queue queue = clCreateCommandQueue( context,device,CL_QUEUE_PROFILING_ENABLE, &error );
if (error != CL_SUCCESS) {
perror("Unable to create command-queue");
exit(1);
}
//forth: load kernel(more than one) and create program to compile it!!!
const char *file_names[] = {"simple.cl", "simple_2.cl"};
const int NUMBER_OF_FILES = 2;
char* buffer[NUMBER_OF_FILES]; /*remember:kernel buffer must be released!*/
size_t sizes[NUMBER_OF_FILES];
loadProgramSource(file_names, NUMBER_OF_FILES, buffer, sizes);
cl_program program = clCreateProgramWithSource(context, NUMBER_OF_FILES, (const char**)buffer, sizes, &error);
if(error != CL_SUCCESS) {
perror("Can't create the OpenCL program object");
return -1;
}
error = clBuildProgram(program, 1, &device, NULL, NULL, NULL);
/* build the program using build-options statically:
const char options[] = "-cl-finite-math-only -cl-no-signed-zeros";
error = clBuildProgram(program, 1, &device, options, NULL, NULL);
There is dynamic solution to build the program by using argv in command line. such as:
error = clBuildProgram(program, 1, &device, argv[1], NULL, NULL);
*/
char *program_log;
size_t log_size;
if(error != CL_SUCCESS) {
clGetProgramBuildInfo(program, device, CL_PROGRAM_BUILD_LOG, 0, NULL, &log_size);
program_log = (char*) malloc(log_size+1);
program_log[log_size] = '\0';
clGetProgramBuildInfo(program, device, CL_PROGRAM_BUILD_LOG,log_size+1, program_log, NULL);
printf("\n=== ERROR ===\n\n%s\n=============\n", program_log);
free(program_log);
return -1;
}
/* Query the program as to how many kernels were detected and how many variables in every kernel function */
cl_uint numOfKernels;
error = clCreateKernelsInProgram(program, 0, NULL, &numOfKernels);
if (error != CL_SUCCESS) {
perror("Unable to retrieve kernel count from program");
exit(1);
}
cl_kernel* kernels = (cl_kernel*) alloca(sizeof(cl_kernel) * numOfKernels);/*once I saw "alloca() can be free automatically",but here?only cl_kernel cannot*/
error = clCreateKernelsInProgram(program, numOfKernels, kernels, NULL);
for(cl_uint i = 0; i < numOfKernels; i++) {
char kernelName[32];
cl_uint argCnt;
clGetKernelInfo(kernels[i], CL_KERNEL_FUNCTION_NAME, sizeof(kernelName), kernelName, NULL);
clGetKernelInfo(kernels[i], CL_KERNEL_NUM_ARGS, sizeof(argCnt), &argCnt, NULL);
printf("Kernel name: %s with arity: %d\n", kernelName, argCnt);
}
//fifth: Buffer (prepare the real arguments of the kernel function.for READ Buffer :Received real arguments from host):
const cl_int mem_size=900;
cl_mem a_in = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_READ_ONLY,mem_size*sizeof(cl_int), NULL, NULL);
cl_mem a_in2 = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_WRITE_ONLY,mem_size*sizeof(cl_int), NULL, NULL);
cl_mem b_in = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_READ_ONLY,mem_size*sizeof(cl_int), NULL, NULL);
cl_mem b_in2 = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_READ_ONLY,mem_size*sizeof(cl_int), NULL, NULL);
cl_mem c_in = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_WRITE_ONLY,mem_size*sizeof(cl_int), NULL, NULL);
cl_mem c_in2 = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_WRITE_ONLY,mem_size*sizeof(cl_int), NULL, NULL);
/*real arguments */
cl_int real_a[mem_size],real_a2[mem_size];
cl_int real_b[mem_size],real_b2[mem_size];
for(cl_int i=0;i<mem_size;i++){
real_a[i]=i;
real_b[i]=mem_size-i;
real_a2[i]=10+i;
real_b2[i]=mem_size-(10+i);
}
error = clEnqueueWriteBuffer (queue , a_in, CL_TRUE,0, mem_size*sizeof(cl_int), real_a,0, NULL, NULL);
error = clEnqueueWriteBuffer (queue , b_in, CL_TRUE,0, mem_size*sizeof(cl_int), real_b,0, NULL, NULL);
error = clEnqueueWriteBuffer (queue , a_in2, CL_TRUE,0, mem_size*sizeof(cl_int), real_a2,0, NULL, NULL);
error = clEnqueueWriteBuffer (queue , b_in2, CL_TRUE,0, mem_size*sizeof(cl_int), real_b2,0, NULL, NULL);
//sixth:send real arguments to kernel function
/* cl_kernel* kernels = (cl_kernel*) alloca(sizeof(cl_kernel) * 2);*/
error = clCreateKernelsInProgram(program, 2, kernels, NULL);
/*Set the arguments of every kernel*/
kernels[0] = clCreateKernel(program, "vectorAdd", NULL);
error = clSetKernelArg(kernels[0], 0, sizeof(cl_mem), (void *) &a_in);
error = clSetKernelArg(kernels[0], 1, sizeof(cl_mem), (void *) &b_in);
error = clSetKernelArg(kernels[0], 2, sizeof(cl_mem), (void *) &c_in);
kernels[1] = clCreateKernel(program, "vectorAdd_2", NULL);
error = clSetKernelArg(kernels[1], 0, sizeof(cl_mem), (void *) &a_in2);
error = clSetKernelArg(kernels[1], 1, sizeof(cl_mem), (void *) &b_in2);
error = clSetKernelArg(kernels[1], 2, sizeof(cl_mem), (void *) &c_in2);
//seventh:set the sizes of Work Items and Work groups,then run the kernels:
/*error = clEnqueueNDRangeKernel(queue, kernels[0], 1, NULL,&global_item_size, &local_item_size, 0, NULL, NULL); when many kernels,use code below:*/
/*error = clEnqueueTask(queue, kernels[0], 0, NULL, NULL);
error = clEnqueueTask(queue, kernels[1], 0, NULL, NULL);*/
size_t global_item_size=mem_size;
size_t local_item_size=1;
error = clEnqueueNDRangeKernel(queue, kernels[0], 1, NULL,&global_item_size, &local_item_size, 0, NULL, NULL);
error = clEnqueueNDRangeKernel(queue, kernels[1], 1, NULL,&global_item_size, &local_item_size, 0, NULL, NULL);
//eighth:copy variables you need to host from device.
cl_int C[mem_size];
error = clEnqueueReadBuffer(queue, c_in, CL_TRUE, 0,mem_size * sizeof(cl_int), C, 0, NULL, NULL);
cl_int C2[mem_size];
error = clEnqueueReadBuffer(queue, c_in2, CL_TRUE, 0,mem_size * sizeof(cl_int), C2, 0, NULL, NULL);
for (cl_uint i = 0; i < mem_size; i++){
printf("%d + %d = %d %d + (%d) = %d\n", real_a[i], real_b[i], C[i],real_a2[i], real_b2[i], C2[i]);
}
//ninth: Clean up
clReleaseCommandQueue(queue);
for(cl_uint i = 0; i < numOfKernels; i++) { clReleaseKernel(kernels[i]); }
for(cl_uint i=0; i< NUMBER_OF_FILES; i++) {
free(buffer[i]);
}
clReleaseProgram(program);
clReleaseContext(context);
error = clReleaseMemObject(a_in);
error = clReleaseMemObject(b_in);
error = clReleaseMemObject(c_in);
error = clReleaseMemObject(a_in2);
error = clReleaseMemObject(b_in2);
error = clReleaseMemObject(c_in2);
return 0;
}
应该哪里我写得有点问题 可能等看了第二章就明白了。
7、《OpenCL Parallel Programming Development CookBook》-Ch2
第一例子 自己写:
#include <CL/cl.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void loadProgramSource(const char** files,
size_t length,
char** buffer,
size_t* sizes) {
/* Read each source file (*.cl) and store the contents into a temporary datastore */
for(size_t i=0; i < length; i++) {
FILE* file = fopen(files[i], "r");
if(file == NULL) {
perror("Couldn't read the program file");
exit(1);
}
fseek(file, 0, SEEK_END);
sizes[i] = ftell(file);
rewind(file); // reset the file pointer so that 'fread' reads from the front
buffer[i] = (char*)malloc(sizes[i]+1);
buffer[i][sizes[i]] = '\0';
fread(buffer[i], sizeof(char), sizes[i], file);
fclose(file);
}
}
typedef struct UserData {
int x;
int y;
int z;
int w;
} UserData;
int main(){
cl_uint platformNum;
cl_int status;
status=clGetPlatformIDs(0,NULL,&platformNum);
if(status!=CL_SUCCESS){
printf("cannot get platforms number.\n");
return -1;
}
cl_platform_id* platforms;
platforms=(cl_platform_id*)alloca(sizeof(cl_platform_id)*platformNum);
status=clGetPlatformIDs(platformNum,platforms,NULL);
if(status!=CL_SUCCESS){
printf("cannot get platforms addresses.\n");
return -1;
}
cl_platform_id platformInUse=platforms[0];
cl_device_id device;
clGetDeviceIDs(platformInUse,CL_DEVICE_TYPE_GPU,1,&device,NULL);
cl_context context=clCreateContext(NULL,1,&device,NULL,NULL,NULL);
cl_command_queue queue=clCreateCommandQueue(context,device,CL_QUEUE_PROFILING_ENABLE, &status);
const char* files[]={"user_test.cl"};
const int kernelnum=1;
char *buffer[kernelnum];
size_t sizes[kernelnum];
loadProgramSource(files, kernelnum, buffer, sizes);
cl_program program=clCreateProgramWithSource(context,kernelnum,(const char**)buffer,sizes,&status);
if(status != CL_SUCCESS) {
perror("Can't create the OpenCL program object");
return -1;
}
status=clBuildProgram(program,1,&device,NULL,NULL,NULL);
if(status != CL_SUCCESS) {
perror("Can't build the OpenCL program object");
return -1;
}
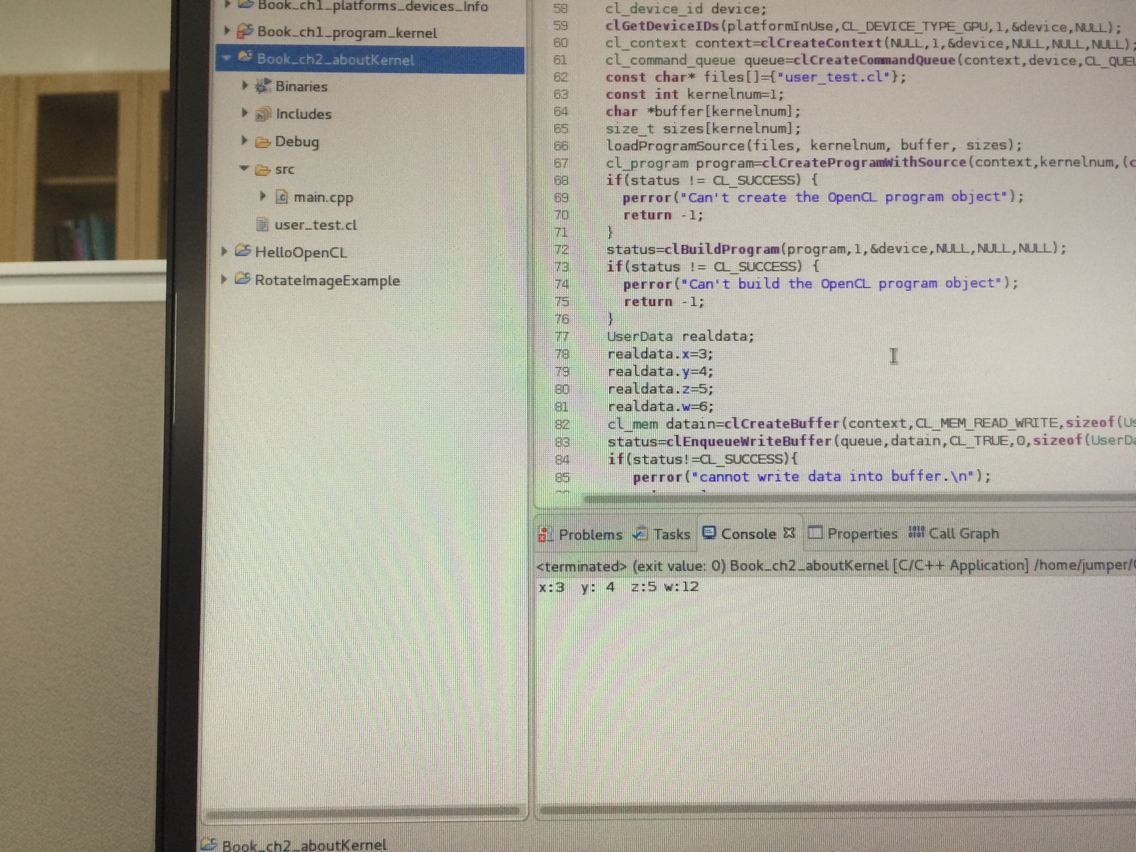
UserData realdata;
realdata.x=3;
realdata.y=4;
realdata.z=5;
realdata.w=6;
cl_mem datain=clCreateBuffer(context,CL_MEM_READ_WRITE,sizeof(UserData),NULL,NULL);
status=clEnqueueWriteBuffer(queue,datain,CL_TRUE,0,sizeof(UserData),&realdata,0,NULL,NULL);
if(status!=CL_SUCCESS){
perror("cannot write data into buffer.\n");
return -1;
}
cl_kernel kernel = clCreateKernel(program, "hello", &status);
status=clSetKernelArg(kernel,0,sizeof(cl_mem),(void*)&datain);
size_t global_item_size=1;
size_t local_item_size=1;
status = clEnqueueNDRangeKernel(queue, kernel, 1, NULL, &global_item_size, &local_item_size, 0, NULL, NULL);
UserData *databack = (UserData*) alloca(sizeof(UserData)) ;
status = clEnqueueReadBuffer(queue, datain, CL_TRUE, 0, sizeof(UserData), databack, 0, NULL, NULL);
printf("x:%d y: %d z:%d w:%d\n", databack->x,databack->y,databack->z,databack->w);
clReleaseCommandQueue(queue);
clReleaseKernel(kernel);
free(buffer[0]);
clReleaseProgram(program);
clReleaseContext(context);
status = clReleaseMemObject(datain);
return 0;
}
刚看了下书上这个例子的源码 它的和我的略不一样 在编译kernel的那个函数 还有实参它有多个实例化后的结构体 我只有一个 到目前为止 我发现我的这个例子虽然对了 但对workItem和workgroup以及device上lobal local的设置还不太会。可能后面就会介绍吧书上。
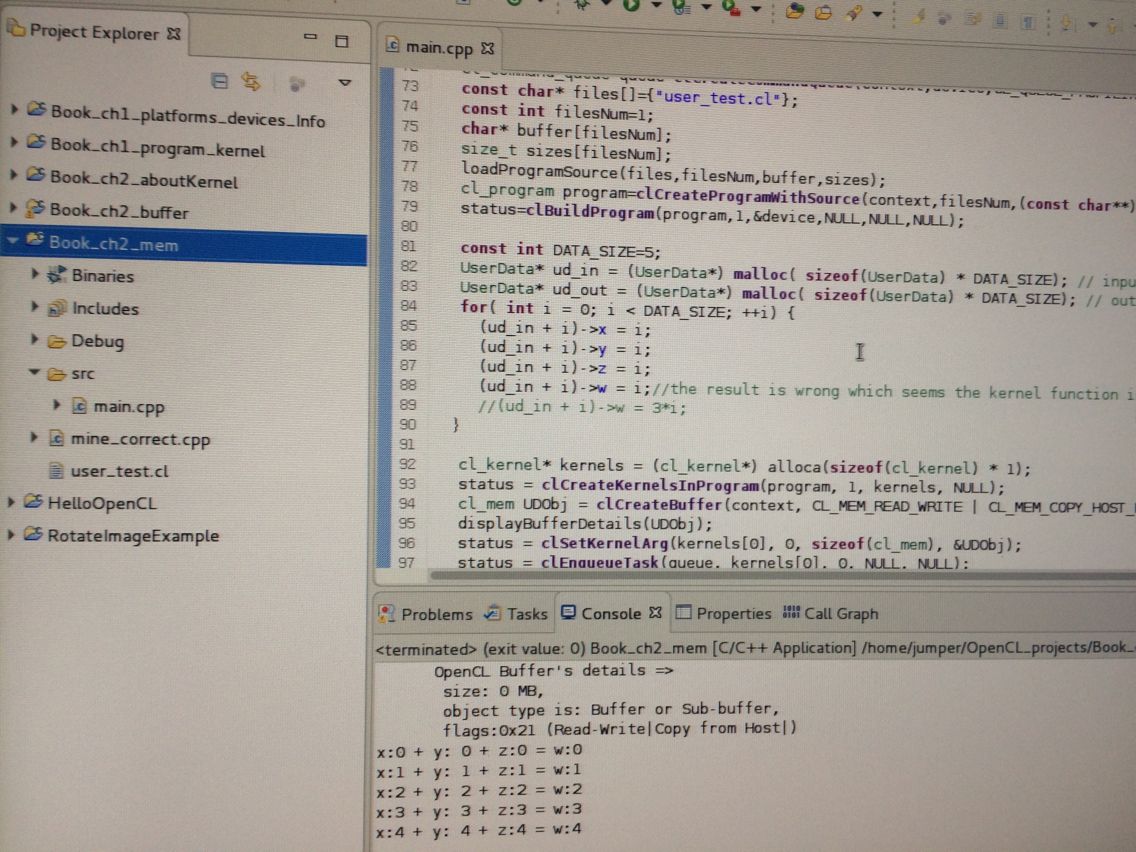
第二个例子:我觉得书上的是错的 因为本该UserData.w是在kernel上计算出来的 所以无论在host上w被初始化成什么经过kernel拷贝回来后一定是正确的x+y+z的结果,不然kernel执行就没有意义了:书上的例子源码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <CL/cl.h>
typedef struct UserData {
int x;
int y;
int z;
int w;
} UserData;
void loadProgramSource(const char** files, size_t length,char** buffer,size_t* sizes) {
/* Read each source file (*.cl) and store the contents into a temporary datastore */
for(size_t i=0; i < length; i++) {
FILE* file = fopen(files[i], "r");
if(file == NULL) {
perror("Couldn't read the program file");
exit(1);
}
fseek(file, 0, SEEK_END);
sizes[i] = ftell(file);
rewind(file); // reset the file pointer so that 'fread' reads from the front
buffer[i] = (char*)malloc(sizes[i]+1);
buffer[i][sizes[i]] = '\0';
fread(buffer[i], sizeof(char), sizes[i], file);
fclose(file);
}
}
void displayBufferDetails(cl_mem memobj) {
cl_mem_object_type objT;
cl_mem_flags flags;
size_t memSize;
clGetMemObjectInfo(memobj, CL_MEM_TYPE, sizeof(cl_mem_object_type), &objT, 0);
clGetMemObjectInfo(memobj, CL_MEM_FLAGS, sizeof(cl_mem_flags), &flags, 0);
clGetMemObjectInfo(memobj, CL_MEM_SIZE, sizeof(size_t), &memSize, 0);
char* str = '\0';
switch (objT) {
case CL_MEM_OBJECT_BUFFER: str = "Buffer or Sub-buffer";break;
case CL_MEM_OBJECT_IMAGE2D: str = "2D Image Object";break;
case CL_MEM_OBJECT_IMAGE3D: str = "3D Image Object";break;
}
char flagStr[128] = {'\0'};
if(flags & CL_MEM_READ_WRITE) strcat(flagStr, "Read-Write|");
if(flags & CL_MEM_WRITE_ONLY) strcat(flagStr, "Write Only|");
if(flags & CL_MEM_READ_ONLY) strcat(flagStr, "Read Only|");
if(flags & CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR) strcat(flagStr, "Copy from Host|");
if(flags & CL_MEM_USE_HOST_PTR) strcat(flagStr, "Use from Host|");
if(flags & CL_MEM_ALLOC_HOST_PTR) strcat(flagStr, "Alloc from Host|");
printf("\tOpenCL Buffer's details =>\n\t size: %lu MB,\n\t object type is: %s,\n\t flags:0x%lx (%s) \n", memSize >> 20, str, flags, flagStr);
}
int main(){
cl_uint platformsNum;
cl_int status;
status=clGetPlatformIDs(0,NULL,&platformsNum);
cl_platform_id *platforms=(cl_platform_id*)alloca(sizeof(cl_platform_id)*platformsNum);
status=clGetPlatformIDs(platformsNum,platforms,NULL);
cl_device_id device;
clGetDeviceIDs(platforms[0],CL_DEVICE_TYPE_GPU,1,&device,NULL);
cl_context context=clCreateContext(NULL,1,&device,NULL,NULL,NULL);
cl_command_queue queue=clCreateCommandQueue(context,device,CL_QUEUE_PROFILING_ENABLE,&status);
const char* files[]={"user_test.cl"};
const int filesNum=1;
char* buffer[filesNum];
size_t sizes[filesNum];
loadProgramSource(files,filesNum,buffer,sizes);
cl_program program=clCreateProgramWithSource(context,filesNum,(const char**)buffer,sizes,&status);
status=clBuildProgram(program,1,&device,NULL,NULL,NULL);
const int DATA_SIZE=5;
UserData* ud_in = (UserData*) malloc( sizeof(UserData) * DATA_SIZE); // input to device
UserData* ud_out = (UserData*) malloc( sizeof(UserData) * DATA_SIZE); // output from device
for( int i = 0; i < DATA_SIZE; ++i) {
(ud_in + i)->x = i;
(ud_in + i)->y = i;
(ud_in + i)->z = i;
(ud_in + i)->w = i;//the result is wrong which seems the kernel function is not significant.
//(ud_in + i)->w = 3*i;
}
cl_kernel* kernels = (cl_kernel*) alloca(sizeof(cl_kernel) * 1);
status = clCreateKernelsInProgram(program, 1, kernels, NULL);
cl_mem UDObj = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_READ_WRITE | CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR, sizeof(UserData) * DATA_SIZE, (void *)ud_in, &status);
displayBufferDetails(UDObj);
status = clSetKernelArg(kernels[0], 0, sizeof(cl_mem), &UDObj);
status = clEnqueueTask(queue, kernels[0], 0, NULL, NULL);
status = clEnqueueReadBuffer(queue, UDObj, CL_TRUE, 0, sizeof(UserData) * DATA_SIZE,ud_out, 0, NULL, NULL);
for(int i=0;i!=DATA_SIZE;i++){
printf("x:%d + y: %d + z:%d = w:%d\n", (ud_out[i]).x,(ud_out[i]).y,(ud_out[i]).z,(ud_out[i]).w);
}
clReleaseCommandQueue(queue);
status = clReleaseMemObject(UDObj);
clReleaseKernel(kernels[0]);
free(buffer[0]);
clReleaseProgram(program);
clReleaseContext(context);
free(ud_in);
free(ud_out);
return 0;
}
我改成了下面这样:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <CL/cl.h>
typedef struct UserData {
int x;
int y;
int z;
int w;
} UserData;
void displayBufferDetails(cl_mem memobj);
void loadProgramSource(const char** files, size_t length,char** buffer,size_t* sizes);
int main(){
cl_uint platformsNum;
cl_int status;
status=clGetPlatformIDs(0,NULL,&platformsNum);
cl_platform_id *platforms=(cl_platform_id*)alloca(sizeof(cl_platform_id)*platformsNum);
status=clGetPlatformIDs(platformsNum,platforms,NULL);
cl_device_id device;
clGetDeviceIDs(platforms[0],CL_DEVICE_TYPE_GPU,1,&device,NULL);
cl_context context=clCreateContext(NULL,1,&device,NULL,NULL,NULL);
cl_command_queue queue=clCreateCommandQueue(context,device,CL_QUEUE_PROFILING_ENABLE,&status);
const char* files[]={"user_test.cl"};
const int filesNum=1;
char* buffer[filesNum];
size_t sizes[filesNum];
loadProgramSource(files,filesNum,buffer,sizes);
cl_program program=clCreateProgramWithSource(context,filesNum,(const char**)buffer,sizes,&status);
status=clBuildProgram(program,1,&device,NULL,NULL,NULL);
const int DATA_SIZE=5;
UserData ud_in[DATA_SIZE] ; // input to device
UserData ud_out[DATA_SIZE]; // output from device
for( int i = 0; i < DATA_SIZE; ++i) {
ud_in[ i].x = i;
ud_in[ i].y = i;
ud_in[ i].z = i;
ud_in[ i].w= i; //the code will always be correct whatever w is.
}
cl_kernel kernel=clCreateKernel(program,"hello",&status);
cl_mem UDObj = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_READ_WRITE | CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR, sizeof(UserData) * DATA_SIZE, (void *)ud_in, &status);
displayBufferDetails(UDObj);
status = clSetKernelArg(kernel, 0, sizeof(cl_mem), &UDObj);
status=clEnqueueWriteBuffer(queue,UDObj,CL_TRUE,0,sizeof(UserData)*DATA_SIZE,ud_in,0,NULL,NULL);
size_t global_item_size=DATA_SIZE;
size_t local_item_size=1;
status = clEnqueueNDRangeKernel(queue, kernel, 1, NULL, &global_item_size, &local_item_size, 0, NULL, NULL);
//status = clEnqueueTask(queue, kernel, 0, NULL, NULL);
status = clEnqueueReadBuffer(queue, UDObj, CL_TRUE, 0, sizeof(UserData)*DATA_SIZE, ud_out, 0, NULL, NULL);
for(int i=0;i!=DATA_SIZE;i++){
printf("x:%d + y: %d + z:%d = w:%d\n", (ud_out[i]).x,(ud_out[i]).y,(ud_out[i]).z,(ud_out[i]).w);
}
clReleaseCommandQueue(queue);
status = clReleaseMemObject(UDObj);
clReleaseKernel(kernel);
free(buffer[0]);
clReleaseProgram(program);
clReleaseContext(context);
return 0;
}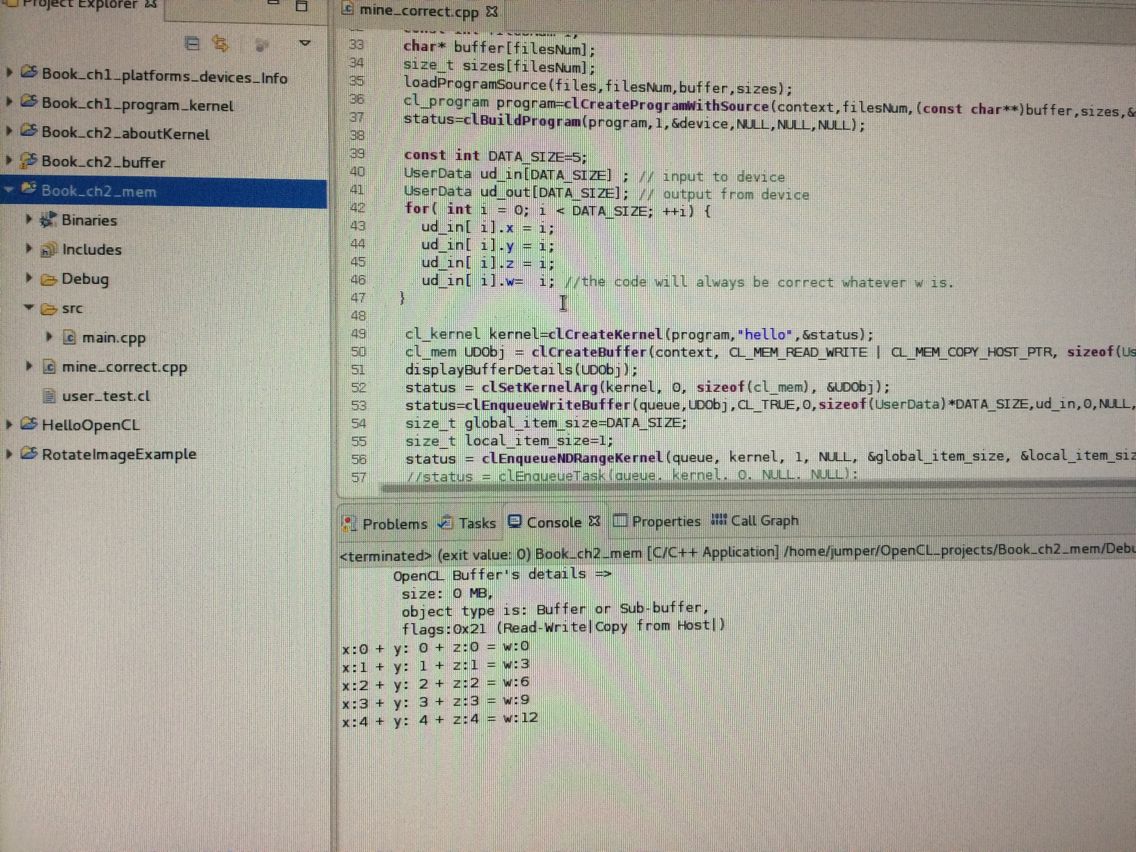
证明是对的 即使在host上被初始化为i 执行kernel后还是正确了 这才有意义嘛
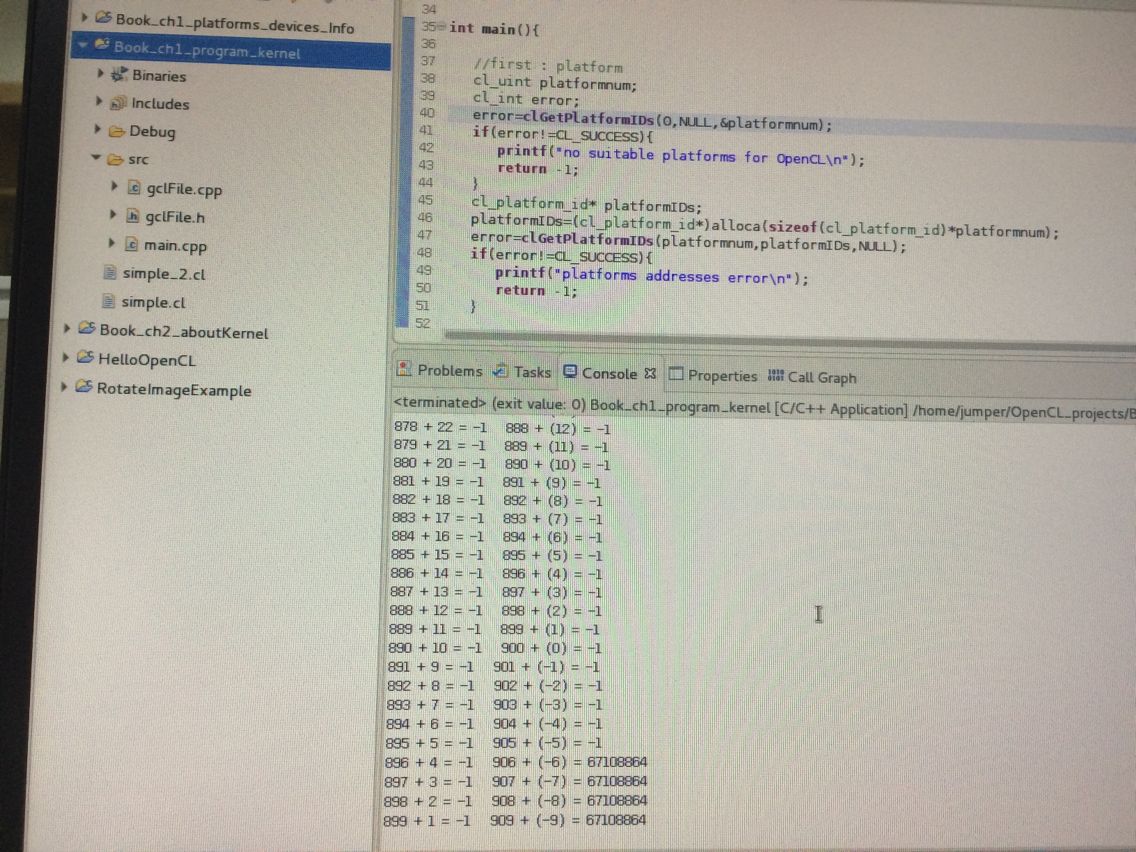
下一个例子是sub-buffer的 我写了下运行了下 和源码对比 原来只有platform或device有多个时才能sub-buffer 不然会报错 我的电脑就是。
再下一个例子是events:延迟command queue中的命令 但这个例子:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <CL/cl.h>
#include <string.h>
void loadProgramSource(const char** files, size_t length,char** buffer,size_t* sizes) {
/* Read each source file (*.cl) and store the contents into a temporary datastore */
for(size_t i=0; i < length; i++) {
FILE* file = fopen(files[i], "r");
if(file == NULL) {
perror("Couldn't read the program file");
exit(1);
}
fseek(file, 0, SEEK_END);
sizes[i] = ftell(file);
rewind(file); // reset the file pointer so that 'fread' reads from the front
buffer[i] = (char*)malloc(sizes[i]+1);
buffer[i][sizes[i]] = '\0';
fread(buffer[i], sizeof(char), sizes[i], file);
fclose(file);
}
}
void CL_CALLBACK postProcess(cl_event event, cl_int status, void *data) {
printf("%s\n", (char*)data);
}
int main(){
cl_uint platformsNum;
cl_int status;
status=clGetPlatformIDs(0,NULL,&platformsNum);
cl_platform_id *platforms=(cl_platform_id*)alloca(sizeof(cl_platform_id)*platformsNum);
status=clGetPlatformIDs(platformsNum,platforms,NULL);
cl_device_id device;
clGetDeviceIDs(platforms[0],CL_DEVICE_TYPE_GPU,1,&device,NULL);
cl_context context=clCreateContext(NULL,1,&device,NULL,NULL,NULL);
cl_command_queue queue=clCreateCommandQueue(context,device,CL_QUEUE_PROFILING_ENABLE,&status);
const char* files[]={"sample_kernel.cl"};
const int filesnum=1;
char* buffer[filesnum];
size_t sizes[filesnum];
loadProgramSource(files,filesnum,buffer,sizes);
cl_program program=clCreateProgramWithSource(context,filesnum,(const char**)buffer,sizes,&status);
status=clBuildProgram(program,1,&device,NULL,NULL,NULL);
int i, j;
float *A;
float *B;
float *C;
A = (float *)alloca(4*4*sizeof(float));
B = (float *)alloca(4*4*sizeof(float));
C = (float *)alloca(4*4*sizeof(float));
for (i=0; i<4; i++) {
for (j=0; j<4; j++) {
A[i*4+j] = i*4+j+1;
B[i*4+j] = j*4+i+1;
}
}
cl_kernel kernel=clCreateKernel(program,"sample",&status);
cl_mem a_buffer=clCreateBuffer(context,CL_MEM_READ_WRITE,sizeof(float)*4*4,NULL,&status);
cl_mem b_buffer=clCreateBuffer(context,CL_MEM_READ_WRITE,sizeof(float)*4*4,NULL,&status);
cl_mem c_buffer=clCreateBuffer(context,CL_MEM_READ_WRITE,sizeof(float)*4*4,NULL,&status);
/*
* Creating an user event
* As a user event is created, its execution status is set to be CL_SUBMITTED
* and we tag the event to a callback so when event reaches CL_COMPLETE, it will
* execute postProcess
*/
cl_event event1 = clCreateUserEvent(context, &status);
char* eventfarg4="Looks like its done.";
clSetEventCallback(event1, CL_COMPLETE, &postProcess, eventfarg4);
status=clSetKernelArg(kernel,0,sizeof(cl_mem),&a_buffer);
status=clSetKernelArg(kernel,0,sizeof(cl_mem),&b_buffer);
status=clSetKernelArg(kernel,0,sizeof(cl_mem),&c_buffer);
status=clEnqueueWriteBuffer(queue,a_buffer,CL_TRUE,0,sizeof(float)*4*4,A,0,NULL,NULL);
//status=clEnqueueWriteBuffer(queue,b_buffer,CL_TRUE,0,sizeof(float)*4*4,B,0,NULL,NULL);
status=clEnqueueWriteBuffer(queue,b_buffer,CL_TRUE,0,sizeof(float)*4*4,B,1,&event1,NULL);
clSetUserEventStatus(event1, CL_COMPLETE);
size_t global_item_size = 4;
size_t local_item_size = 1;
status = clEnqueueNDRangeKernel(queue, kernel, 1, NULL, &global_item_size, &local_item_size, 0, NULL, NULL);
status = clEnqueueReadBuffer(queue, c_buffer, CL_TRUE, 0, 4*4*sizeof(float), C, 0, NULL, NULL);
for (i=0; i<4; i++) {
for (j=0; j<4; j++) {
printf("%7.2f ", C[i*4+j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
clReleaseCommandQueue(queue);
clReleaseKernel(kernel);
clReleaseProgram(program);
clReleaseMemObject(a_buffer);
clReleaseMemObject(b_buffer);
clReleaseMemObject(c_buffer);
clReleaseContext(context);
clReleaseEvent(event1);
return 0;
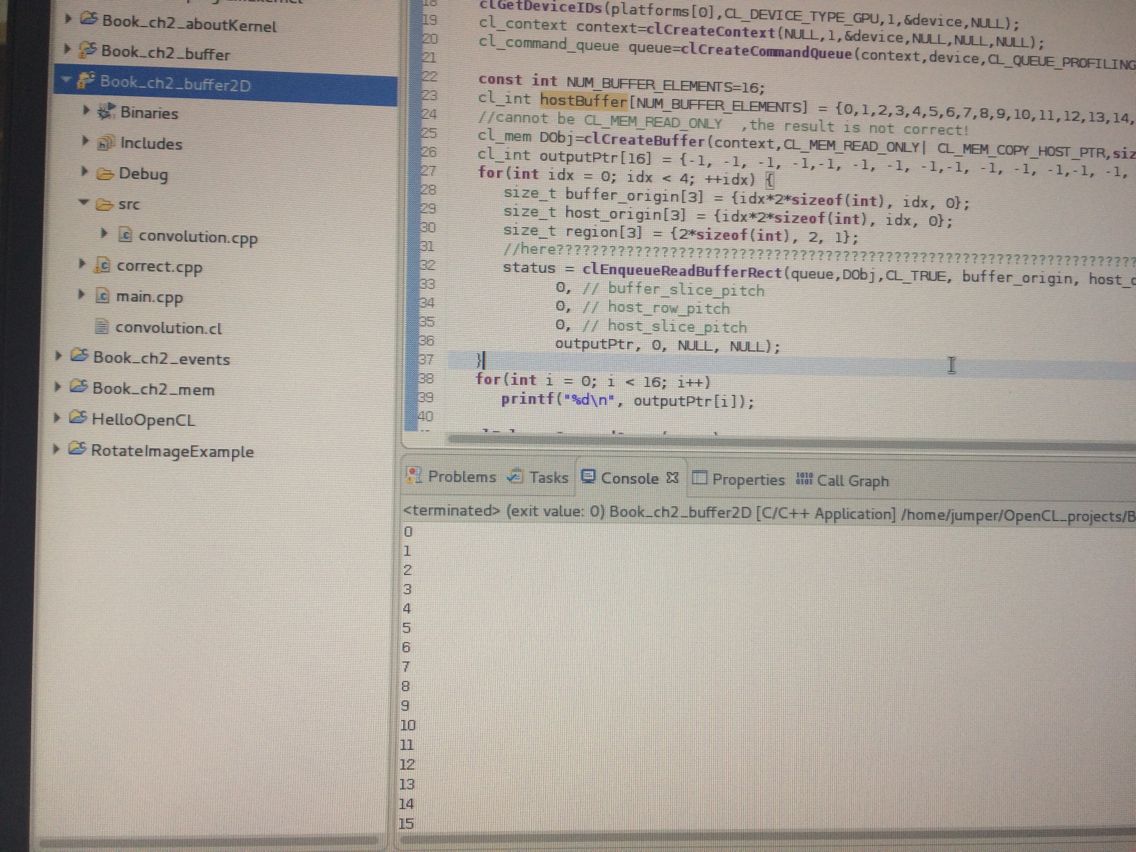
}下一个例子是创建2D buffer_memory的 第一次看到这种不用读kernel的 那这种有什么意义呢用OpenCL 怎么去加速呢?是不是只要有buffer就可以实现加速了?
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <CL/cl.h>
int main(){
cl_uint platformsNum;
cl_int status;
status=clGetPlatformIDs(0,NULL,&platformsNum);
cl_platform_id *platforms=(cl_platform_id*)alloca(sizeof(cl_platform_id)*platformsNum);
status=clGetPlatformIDs(platformsNum,platforms,NULL);
cl_device_id device;
clGetDeviceIDs(platforms[0],CL_DEVICE_TYPE_GPU,1,&device,NULL);
cl_context context=clCreateContext(NULL,1,&device,NULL,NULL,NULL);
cl_command_queue queue=clCreateCommandQueue(context,device,CL_QUEUE_PROFILING_ENABLE,&status);
const int NUM_BUFFER_ELEMENTS=16;
cl_int hostBuffer[NUM_BUFFER_ELEMENTS] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15};
//cannot be CL_MEM_READ_ONLY ,the result is not correct!
cl_mem DObj=clCreateBuffer(context,CL_MEM_READ_ONLY| CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR,sizeof(int)*NUM_BUFFER_ELEMENTS,hostBuffer,&status);
cl_int outputPtr[16] = {-1, -1, -1, -1,-1, -1, -1, -1,-1, -1, -1, -1,-1, -1, -1, -1};
for(int idx = 0; idx < 4; ++idx) {
size_t buffer_origin[3] = {idx*2*sizeof(int), idx, 0};
size_t host_origin[3] = {idx*2*sizeof(int), idx, 0};
size_t region[3] = {2*sizeof(int), 2, 1};
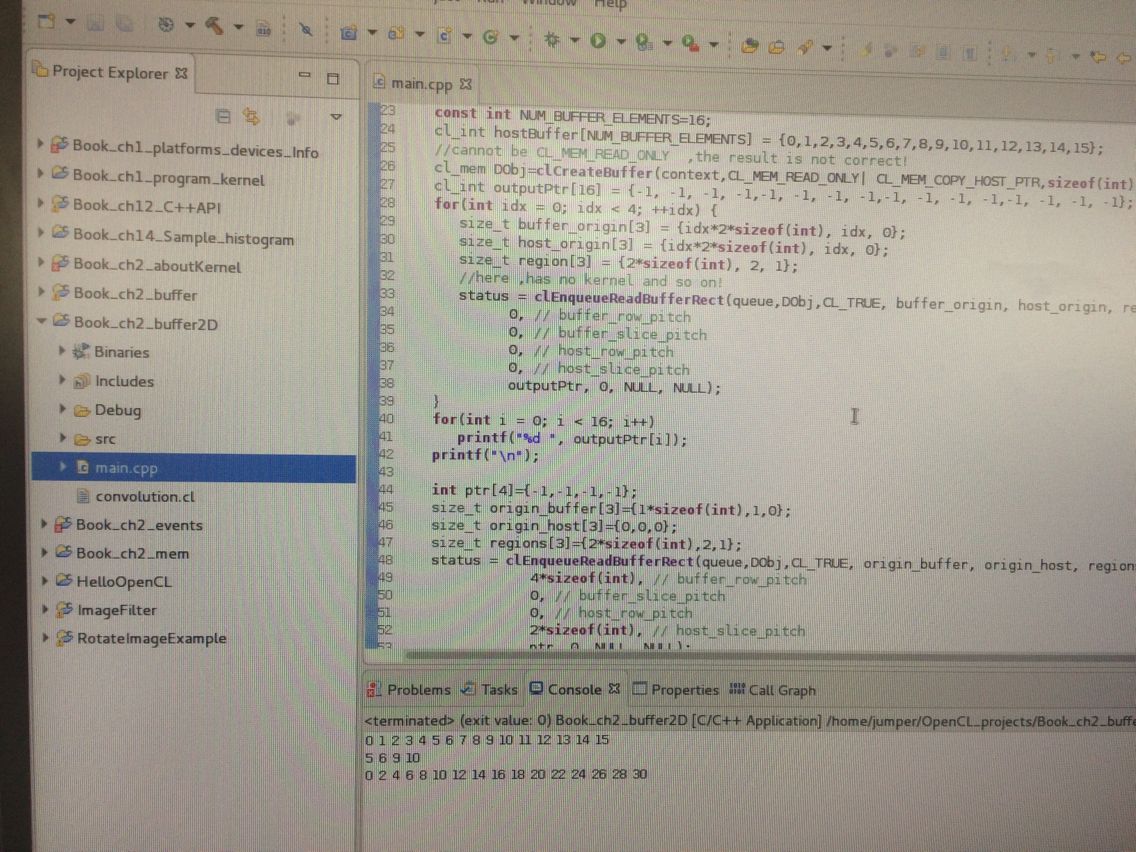
//here????????????????????has no kernel and so on but it can get correct results!
status = clEnqueueReadBufferRect(queue,DObj,CL_TRUE, buffer_origin, host_origin, region,
0, // buffer_row_pitch
0, // buffer_slice_pitch
0, // host_row_pitch
0, // host_slice_pitch
outputPtr, 0, NULL, NULL);
}
for(int i = 0; i < 16; i++)
printf("%d\n", outputPtr[i]);
clReleaseCommandQueue(queue);
status = clReleaseMemObject(DObj);
clReleaseContext(context);
return 0;
}
下个例子我补的是《OpenCL编程思想》的卷积:也是二维的例子 可以看成图像:
int main(){
cl_uint platformsNum;
cl_int status;
status=clGetPlatformIDs(0,NULL,&platformsNum);
cl_platform_id *platforms=(cl_platform_id*)alloca(sizeof(cl_platform_id)*platformsNum);
status=clGetPlatformIDs(platformsNum,platforms,NULL);
cl_device_id device;
clGetDeviceIDs(platforms[0],CL_DEVICE_TYPE_GPU,1,&device,NULL);
cl_context context=clCreateContext(NULL,1,&device,NULL,NULL,NULL);
cl_command_queue queue=clCreateCommandQueue(context,device,CL_QUEUE_PROFILING_ENABLE,&status);
const char* filelist[]={"convolution.cl"};
const int filenum=1;
char* buffer[filenum];
size_t sizes[filenum];
loadProgramSource(filelist,filenum,buffer,sizes);
cl_program program=clCreateProgramWithSource(context,filenum,(const char**)buffer,sizes,&status);
status=clBuildProgram(program,1,&device,NULL,NULL,NULL);
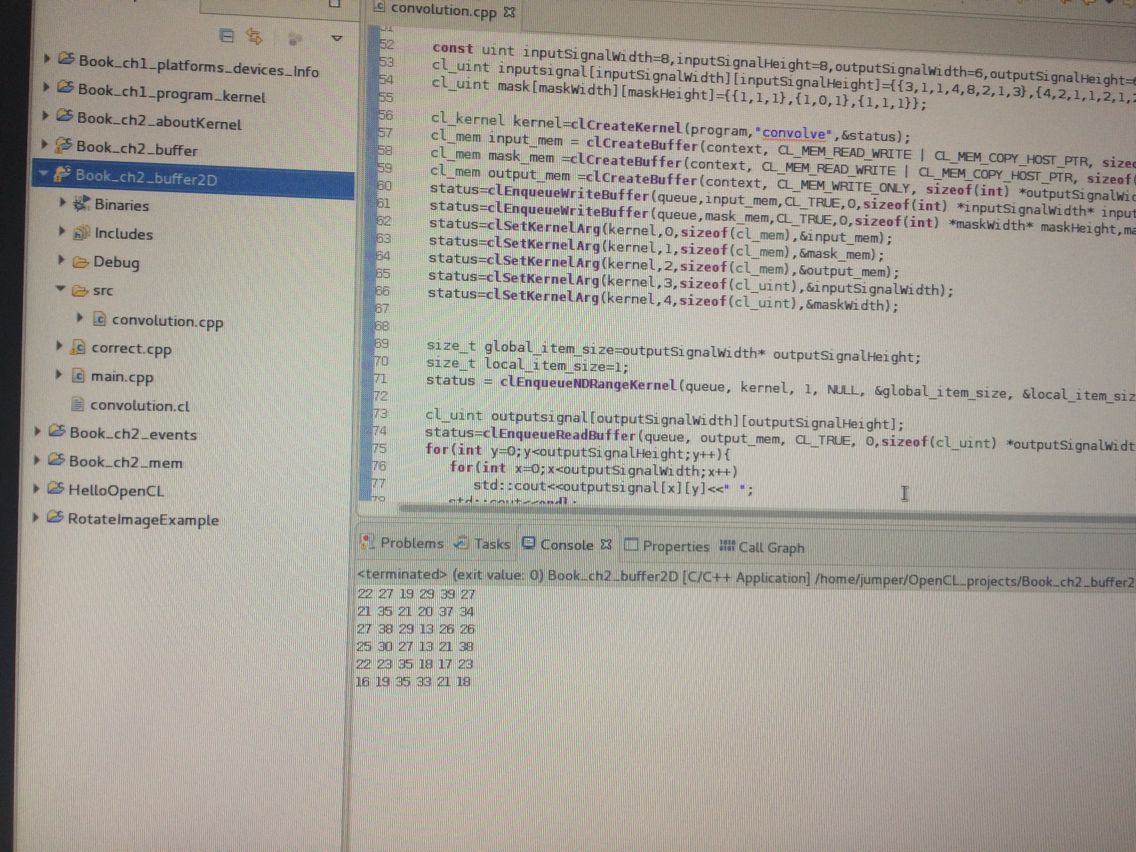
const uint inputSignalWidth=8,inputSignalHeight=8,outputSignalWidth=6,outputSignalHeight=6,maskWidth=3,maskHeight=3;
cl_uint inputsignal[inputSignalWidth][inputSignalHeight]={
{3,1,1,4,8,2,1,3},{4,2,1,1,2,1,2,3},{4,4,4,4,3,2,2,2},{9,8,6,4,2,3,4,4},{1,1,6,4,0,0,0,0},{0,9,0,5,3,0,5,5},{8,6,4,3,3,3,1,1,},{5,6,0,0,0,0,6,2}};
cl_uint mask[maskWidth][maskHeight]={
{1,1,1},{1,0,1},{1,1,1}};
cl_kernel kernel=clCreateKernel(program,"convolve",&status);
cl_mem input_mem = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_READ_WRITE | CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR, sizeof(int) *inputSignalWidth* inputSignalHeight,inputsignal, &status);
cl_mem mask_mem =clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_READ_WRITE | CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR, sizeof(int) *maskWidth* maskHeight, mask, &status);
cl_mem output_mem =clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_WRITE_ONLY, sizeof(int) *outputSignalWidth* outputSignalHeight, NULL, &status);
status=clEnqueueWriteBuffer(queue,input_mem,CL_TRUE,0,sizeof(int) *inputSignalWidth* inputSignalHeight,inputsignal,0,NULL,NULL);
status=clEnqueueWriteBuffer(queue,mask_mem,CL_TRUE,0,sizeof(int) *maskWidth* maskHeight,mask,0,NULL,NULL);
status=clSetKernelArg(kernel,0,sizeof(cl_mem),&input_mem);
status=clSetKernelArg(kernel,1,sizeof(cl_mem),&mask_mem);
status=clSetKernelArg(kernel,2,sizeof(cl_mem),&output_mem);
status=clSetKernelArg(kernel,3,sizeof(cl_uint),&inputSignalWidth);
status=clSetKernelArg(kernel,4,sizeof(cl_uint),&maskWidth);
size_t global_item_size=outputSignalWidth* outputSignalHeight;
size_t local_item_size=1;
status = clEnqueueNDRangeKernel(queue, kernel, 1, NULL, &global_item_size, &local_item_size, 0, NULL, NULL);
cl_uint outputsignal[outputSignalWidth][outputSignalHeight];
status=clEnqueueReadBuffer(queue, output_mem, CL_TRUE, 0,sizeof(cl_uint) *outputSignalWidth* outputSignalHeight, outputsignal, 0, NULL, NULL);
for(int y=0;y<outputSignalHeight;y++){
for(int x=0;x<outputSignalWidth;x++)
std::cout<<outputsignal[x][y]<<" ";
std::cout<<endl;
}
clReleaseCommandQueue(queue);
status = clReleaseMemObject(input_mem);
status = clReleaseMemObject(mask_mem);
status = clReleaseMemObject(output_mem);
clReleaseKernel(kernel);
clReleaseProgram(program);
clReleaseContext(context);
return 0;
}
__kernel void convolve(const __global uint* const input,__constant uint* const mask,__global uint* output,const int inputWidth,const int maskWidth){
const int x=get_global_id(0);
const int y=get_global_id(1);
uint sum=0;
for(int r=0;r<maskWidth;r++){
const int tempIdx=(y+r)*inputWidth+x;
for(int c=0;c<maskWidth;c++)
sum+=mask[(r*maskWidth)+c]*input[tempIdx+c];
}
output[y*get_global_size(0)+x]=sum;
}现在看到《OpenCL编程指南》第9章 上面这个核函数的问题我自己已明白 通过第8章的一个例子:高斯滤波 改动:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <CL/cl.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include "FreeImage.h"
#include "gFreeImage.h"
cl_mem LoadImage(cl_context context, char *fileName, int &width, int &height)
{
FREE_IMAGE_FORMAT format = FreeImage_GetFileType(fileName, 0);
FIBITMAP* image = FreeImage_Load(format, fileName);
// Convert to 32-bit image
FIBITMAP* temp = image;
image = FreeImage_ConvertTo32Bits(image);
FreeImage_Unload(temp);
width = FreeImage_GetWidth(image);
height = FreeImage_GetHeight(image);
char *buffer = new char[width * height * 4];
memcpy(buffer, FreeImage_GetBits(image), width * height * 4);
FreeImage_Unload(image);
// Create OpenCL image
cl_image_format clImageFormat;
clImageFormat.image_channel_order = CL_RGBA;
clImageFormat.image_channel_data_type = CL_UNORM_INT8;
cl_int errNum;
cl_mem clImage;
clImage = clCreateImage2D(context, CL_MEM_READ_ONLY | CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR,&clImageFormat,width,height, 0,buffer,&errNum);
if (errNum != CL_SUCCESS)
{
std::cerr << "Error creating CL image object" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
return clImage;
}
size_t RoundUp(int groupSize, int globalSize)
{
int r = globalSize % groupSize;
if(r == 0)
{
return globalSize;
}
else
{
return globalSize + groupSize - r;
}
}
bool SaveImage(char *fileName, char *buffer, int width, int height)
{
FREE_IMAGE_FORMAT format = FreeImage_GetFIFFromFilename(fileName);
FIBITMAP *image = FreeImage_ConvertFromRawBits((BYTE*)buffer, width,
height, width * 4, 32,
0xFF000000, 0x00FF0000, 0x0000FF00);
return (FreeImage_Save(format, image, fileName) == TRUE) ? true : false;
}
int main(){
cl_uint platformNum;
cl_int status;
status=clGetPlatformIDs(0,NULL,&platformNum);
if(status!=CL_SUCCESS){
printf("cannot get platforms number.\n");
return -1;
}
cl_platform_id* platforms;
platforms=(cl_platform_id*)alloca(sizeof(cl_platform_id)*platformNum);
status=clGetPlatformIDs(platformNum,platforms,NULL);
if(status!=CL_SUCCESS){
printf("cannot get platforms addresses.\n");
return -1;
}
cl_platform_id platformInUse=platforms[0];
cl_device_id device;
clGetDeviceIDs(platformInUse,CL_DEVICE_TYPE_GPU,1,&device,NULL);
cl_context context=clCreateContext(NULL,1,&device,NULL,NULL,NULL);
cl_command_queue queue=clCreateCommandQueue(context,device,CL_QUEUE_PROFILING_ENABLE, &status);
//Create Input Image Object
char file[]={"sample_raw.png"};
int imgwidth,imgheight;
cl_mem image=LoadImage(context,file,imgwidth,imgheight);
cl_image_format clImageFormat;
//Create Output Image Object
clImageFormat.image_channel_order = CL_RGBA;
clImageFormat.image_channel_data_type = CL_UNORM_INT8;
cl_mem outimg;
outimg = clCreateImage2D(context, CL_MEM_WRITE_ONLY,&clImageFormat,imgwidth,imgheight, 0,NULL,&status);
//Create Image Sampler
cl_sampler sampler=clCreateSampler(context,CL_FALSE, CL_ADDRESS_CLAMP_TO_EDGE,CL_FILTER_NEAREST,&status);
std::ifstream srcFile("ImageFilter2D.cl");
std::string srcProg(std::istreambuf_iterator<char>(srcFile),(std::istreambuf_iterator<char>()));
const char * src = srcProg.c_str();
size_t length = srcProg.length();
cl_program program=clCreateProgramWithSource(context,1,&src,&length,&status);
status=clBuildProgram(program,1,&device,NULL,NULL,NULL);
cl_kernel kernel=clCreateKernel(program,"gaussian_filter",NULL);
status = clSetKernelArg(kernel, 0, sizeof(cl_mem), &image);
status |= clSetKernelArg(kernel, 1, sizeof(cl_mem), &outimg);
status |= clSetKernelArg(kernel, 2, sizeof(cl_sampler), &sampler);
status |= clSetKernelArg(kernel, 3, sizeof(cl_int), &imgwidth);
status |= clSetKernelArg(kernel, 4, sizeof(cl_int), &imgheight);
size_t localWorkSize[2] = { 16, 16 };
size_t globalWorkSize[2] = { RoundUp(localWorkSize[0], imgwidth),RoundUp(localWorkSize[1], imgheight) };
status=clEnqueueNDRangeKernel(queue,kernel,2, NULL,globalWorkSize, localWorkSize,0, NULL, NULL);
// char *buffer = (char*)alloca[imgwidth * imgheight * 4]; //wrong !!!!
char *buffer = (char*)alloca(imgwidth * imgheight * 4);
size_t origin[3] = { 0, 0, 0 };
size_t region[3] = { imgwidth, imgheight, 1};
status = clEnqueueReadImage(queue, outimg, CL_TRUE,origin, region, 0, 0, buffer,0, NULL, NULL);
char imgname[]={"filteredimg.png"};
bool flag=SaveImage(imgname, buffer, imgwidth, imgheight);
clReleaseCommandQueue(queue);
clReleaseContext(context);
clReleaseProgram(program);
clReleaseKernel(kernel);
clReleaseMemObject(image);
clReleaseMemObject(outimg);
clReleaseSampler(sampler);
return 0;
}它的kernel:
__kernel void gaussian_filter(__read_only image2d_t srcImg,__write_only image2d_t dstImg,sampler_t sampler,int width, int height)
{
float kernelWeights[9] = { 1.0f, 2.0f, 1.0f,
2.0f, 4.0f, 2.0f,
1.0f, 2.0f, 1.0f };
int2 startImageCoord = (int2) (get_global_id(0) - 1, get_global_id(1) - 1);
int2 endImageCoord = (int2) (get_global_id(0) + 1, get_global_id(1) + 1);
int2 outImageCoord = (int2) (get_global_id(0), get_global_id(1));
if (outImageCoord.x < width && outImageCoord.y < height)
{
int weight = 0;
float4 outColor = (float4)(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
for( int y = startImageCoord.y; y <= endImageCoord.y; y++)
{
for( int x = startImageCoord.x; x <= endImageCoord.x; x++)
{
outColor += (read_imagef(srcImg, sampler, (int2)(x, y)) * (kernelWeights[weight] / 16.0f));
weight += 1;
}
}
// Write the output value to image
write_imagef(dstImg, outImageCoord, outColor);
}
}
所以之前没有想明白的问题 也就是之前那个卷积的kernel我也想明白了 还有我查了下 get_global_size(0)是什么意思了 原来是指每个工作组x方向上占多大即多少个workitems。这个高斯滤波奇怪之处在于我开始用一幅图处理结果竟然是个白纸 !有问题 但我换了一幅图就好了。即使直接用书上源码 不用我上面那个也是这样!奇怪!
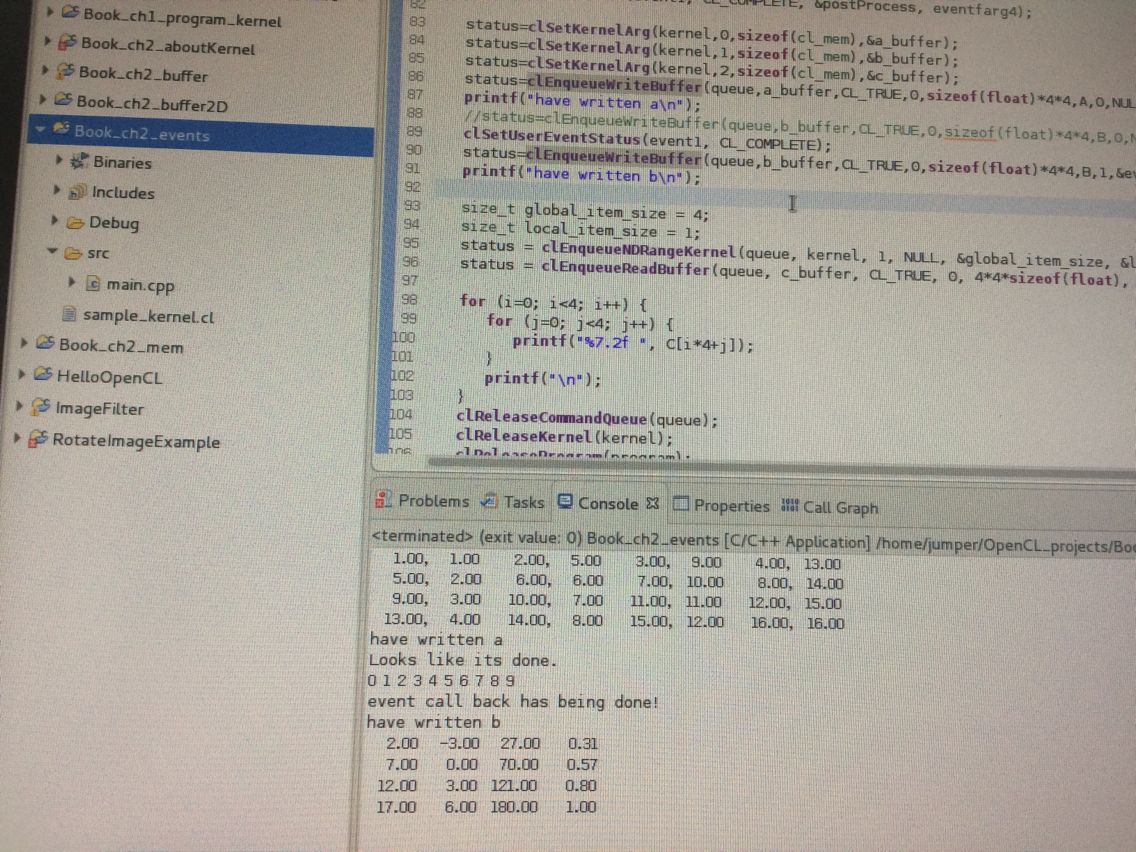
看到《OpenCL编程指南》第9.5节 其实第9章我没怎么理解 因为没有什么实例供我学习。但看到这里 我知道我之前的那个event的工程为什么错了 首先源代码中的意思是向buffer中传入B参数时host创建了一个event 这个事件会回调一个异步函数 等这个event标志被host调为CL_COMPLETE后就继续执行写入B_buffer和执行kernel。它位置放错了set CL_COMPLETE位置放在后面了 所以那句写B等待一直读不到CL_COMPLETE所以一直卡在那里!还有一个就是我粗心写错的 就是SetKernel那里 我改过来了。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <CL/cl.h>
#include <string.h>
void loadProgramSource(const char** files, size_t length,char** buffer,size_t* sizes) {
/* Read each source file (*.cl) and store the contents into a temporary datastore */
for(size_t i=0; i < length; i++) {
FILE* file = fopen(files[i], "r");
if(file == NULL) {
perror("Couldn't read the program file");
exit(1);
}
fseek(file, 0, SEEK_END);
sizes[i] = ftell(file);
rewind(file); // reset the file pointer so that 'fread' reads from the front
buffer[i] = (char*)malloc(sizes[i]+1);
buffer[i][sizes[i]] = '\0';
fread(buffer[i], sizeof(char), sizes[i], file);
fclose(file);
}
}
void CL_CALLBACK postProcess(cl_event event, cl_int status, void *data) {
printf("%s\n", (char*)data);
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
printf("%d ",i);
printf("\nevent call back has being done!\n");
}
int main(){
cl_uint platformsNum;
cl_int status;
status=clGetPlatformIDs(0,NULL,&platformsNum);
cl_platform_id *platforms=(cl_platform_id*)alloca(sizeof(cl_platform_id)*platformsNum);
status=clGetPlatformIDs(platformsNum,platforms,NULL);
cl_device_id device;
clGetDeviceIDs(platforms[0],CL_DEVICE_TYPE_GPU,1,&device,NULL);
cl_context context=clCreateContext(NULL,1,&device,NULL,NULL,NULL);
cl_command_queue queue=clCreateCommandQueue(context,device,CL_QUEUE_PROFILING_ENABLE,&status);
const char* files[]={"sample_kernel.cl"};
const int filesnum=1;
char* buffer[filesnum];
size_t sizes[filesnum];
loadProgramSource(files,filesnum,buffer,sizes);
cl_program program=clCreateProgramWithSource(context,filesnum,(const char**)buffer,sizes,&status);
status=clBuildProgram(program,1,&device,NULL,NULL,NULL);
int i, j;
float *A = (float *)alloca(4*4*sizeof(float));
float *B = (float *)alloca(4*4*sizeof(float));
float *C = (float *)alloca(4*4*sizeof(float));
for (i=0; i<4; i++) {
for (j=0; j<4; j++) {
A[i*4+j] = i*4+j+1;
B[i*4+j] = j*4+i+1;
printf("%7.2f,%7.2f ", A[i*4+j],B[i*4+j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
cl_kernel kernel=clCreateKernel(program,"sample",&status);
cl_mem a_buffer=clCreateBuffer(context,CL_MEM_READ_WRITE,sizeof(float)*4*4,NULL,&status);
cl_mem b_buffer=clCreateBuffer(context,CL_MEM_READ_WRITE,sizeof(float)*4*4,NULL,&status);
cl_mem c_buffer=clCreateBuffer(context,CL_MEM_READ_WRITE,sizeof(float)*4*4,NULL,&status);
/*
* Creating an user event
* As a user event is created, its execution status is set to be CL_SUBMITTED
* and we tag the event to a callback so when event reaches CL_COMPLETE, it will
* execute postProcess
*/
cl_event event1 = clCreateUserEvent(context, &status);
char* eventfarg4="Looks like its done.";
clSetEventCallback(event1, CL_COMPLETE, &postProcess, eventfarg4);
status=clSetKernelArg(kernel,0,sizeof(cl_mem),&a_buffer);
status=clSetKernelArg(kernel,1,sizeof(cl_mem),&b_buffer);
status=clSetKernelArg(kernel,2,sizeof(cl_mem),&c_buffer);
status=clEnqueueWriteBuffer(queue,a_buffer,CL_TRUE,0,sizeof(float)*4*4,A,0,NULL,NULL);
printf("have written a\n");
//status=clEnqueueWriteBuffer(queue,b_buffer,CL_TRUE,0,sizeof(float)*4*4,B,0,NULL,NULL);
clSetUserEventStatus(event1, CL_COMPLETE);
status=clEnqueueWriteBuffer(queue,b_buffer,CL_TRUE,0,sizeof(float)*4*4,B,1,&event1,NULL);
printf("have written b\n");
size_t global_item_size = 4;
size_t local_item_size = 1;
status = clEnqueueNDRangeKernel(queue, kernel, 1, NULL, &global_item_size, &local_item_size, 0, NULL, NULL);
status = clEnqueueReadBuffer(queue, c_buffer, CL_TRUE, 0, 4*4*sizeof(float), C, 0, NULL, NULL);
for (i=0; i<4; i++) {
for (j=0; j<4; j++) {
printf("%7.2f ", C[i*4+j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
clReleaseCommandQueue(queue);
clReleaseKernel(kernel);
clReleaseProgram(program);
clReleaseMemObject(a_buffer);
clReleaseMemObject(b_buffer);
clReleaseMemObject(c_buffer);
clReleaseContext(context);
clReleaseEvent(event1);
return 0;
}
通过这个例子 我理解了host创建event 回调函数显示控制commandqueue中的命令顺序 !但第9章所说的跨不同context和queue的交互我没怎么懂、同步点那里也没怎么懂!没实例!
还有一个例子 就是之前我说clEnqueueReadBufferRect()中第7、8、9和10个参数我不懂的 看了书上后懂了意思,书上给了计算公式 套公式就行。这个例子是不进入kernel而是直接在buffer进行计算:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <CL/cl.h>
//?????????????????
int main(){
cl_uint platformsNum;
cl_int status;
status=clGetPlatformIDs(0,NULL,&platformsNum);
cl_platform_id *platforms=(cl_platform_id*)alloca(sizeof(cl_platform_id)*platformsNum);
status=clGetPlatformIDs(platformsNum,platforms,NULL);
cl_device_id device;
clGetDeviceIDs(platforms[0],CL_DEVICE_TYPE_GPU,1,&device,NULL);
cl_context context=clCreateContext(NULL,1,&device,NULL,NULL,NULL);
cl_command_queue queue=clCreateCommandQueue(context,device,CL_QUEUE_PROFILING_ENABLE,&status);
const int NUM_BUFFER_ELEMENTS=16;
cl_int hostBuffer[NUM_BUFFER_ELEMENTS] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15};
//cannot be CL_MEM_READ_ONLY ,the result is not correct!
cl_mem DObj=clCreateBuffer(context,CL_MEM_READ_ONLY| CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR,sizeof(int)*NUM_BUFFER_ELEMENTS,hostBuffer,&status);
cl_int outputPtr[16] = {-1, -1, -1, -1,-1, -1, -1, -1,-1, -1, -1, -1,-1, -1, -1, -1};
for(int idx = 0; idx < 4; ++idx) {
size_t buffer_origin[3] = {idx*2*sizeof(int), idx, 0};
size_t host_origin[3] = {idx*2*sizeof(int), idx, 0};
size_t region[3] = {2*sizeof(int), 2, 1};
//here ,has no kernel and so on!
status = clEnqueueReadBufferRect(queue,DObj,CL_TRUE, buffer_origin, host_origin, region,
0, // buffer_row_pitch
0, // buffer_slice_pitch
0, // host_row_pitch
0, // host_slice_pitch
outputPtr, 0, NULL, NULL);
}
for(int i = 0; i < 16; i++)
printf("%d ", outputPtr[i]);
printf("\n");
int ptr[4]={-1,-1,-1,-1};
size_t origin_buffer[3]={1*sizeof(int),1,0};
size_t origin_host[3]={0,0,0};
size_t regions[3]={2*sizeof(int),2,1};
status = clEnqueueReadBufferRect(queue,DObj,CL_TRUE, origin_buffer, origin_host, regions,
4*sizeof(int), // buffer_row_pitch
0, // buffer_slice_pitch
0, // host_row_pitch
2*sizeof(int), // host_slice_pitch
ptr, 0, NULL, NULL);
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
printf("%d ", ptr[i]); //I can calculate "5" ,but why the sequence is 6 9 10?????????
printf("\n");
//do not use clEnqueueReadBuffer() or clEnqueueReadBufferRect() but clEnqueueMapBuffer() and clEnqueueUnmapMemObject()
cl_int *mapptr=(cl_int*)clEnqueueMapBuffer(queue,DObj,CL_TRUE,CL_MAP_WRITE,0,sizeof(cl_int)*NUM_BUFFER_ELEMENTS,0,NULL,NULL,&status);
for(uint i=0;i<NUM_BUFFER_ELEMENTS;i++){
mapptr[i]=i*2;
}
status=clEnqueueUnmapMemObject(queue,DObj,mapptr,0,NULL,NULL);
clFinish(queue);
cl_int *mapedptr=(cl_int*)clEnqueueMapBuffer(queue,DObj,CL_TRUE,CL_MAP_READ,0,sizeof(cl_int)*NUM_BUFFER_ELEMENTS,0,NULL,NULL,&status);
cl_int *hostptr=(cl_int*)alloca(sizeof(cl_int)*NUM_BUFFER_ELEMENTS);
for(uint j=0;j<NUM_BUFFER_ELEMENTS;j++)
hostptr[j]=mapptr[j];
status=clEnqueueUnmapMemObject(queue,DObj,hostptr,0,NULL,NULL);
clFinish(queue);
for(int i = 0; i < 16; i++)
printf("%d ", hostptr[i]);
clReleaseCommandQueue(queue);
status = clReleaseMemObject(DObj);
clReleaseContext(context);
return 0;
}第一行和第三行的结果直接套公式就知道。但第二行的结果 我套公式只能算出5, 那个6 9 10怎么计算来的 我没懂????????
看到性能评估这一章:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <CL/cl.h>
#include <string.h>
void loadProgramSource(const char** files, size_t length,char** buffer,size_t* sizes);
void CL_CALLBACK eventCallBack(cl_event ev,cl_int event_status,void* user_data);
int main(){
cl_uint platformsNum;
cl_int status;
status=clGetPlatformIDs(0,NULL,&platformsNum);
cl_platform_id *platforms=(cl_platform_id*)alloca(sizeof(cl_platform_id)*platformsNum);
status=clGetPlatformIDs(platformsNum,platforms,NULL);
cl_device_id device;
clGetDeviceIDs(platforms[0],CL_DEVICE_TYPE_GPU,1,&device,NULL);
cl_context context=clCreateContext(NULL,1,&device,NULL,NULL,NULL);
cl_command_queue queue=clCreateCommandQueue(context,device,CL_QUEUE_PROFILING_ENABLE,&status);
const char* files[]={"sample_kernel.cl"};
const int filesnum=1;
char* buffer[filesnum];
size_t sizes[filesnum];
loadProgramSource(files,filesnum,buffer,sizes);
cl_program program=clCreateProgramWithSource(context,filesnum,(const char**)buffer,sizes,&status);
status=clBuildProgram(program,1,&device,NULL,NULL,NULL);
int i, j;
float *A = (float *)alloca(4*4*sizeof(float));
float *B = (float *)alloca(4*4*sizeof(float));
float *C = (float *)alloca(4*4*sizeof(float));
for (i=0; i<4; i++) {
for (j=0; j<4; j++) {
A[i*4+j] = i*4+j+1;
B[i*4+j] = j*4+i+1;
printf("%7.2f,%7.2f ", A[i*4+j],B[i*4+j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
cl_kernel kernel=clCreateKernel(program,"sample",&status);
cl_mem a_buffer=clCreateBuffer(context,CL_MEM_READ_WRITE,sizeof(float)*4*4,NULL,&status);
cl_mem b_buffer=clCreateBuffer(context,CL_MEM_READ_WRITE,sizeof(float)*4*4,NULL,&status);
cl_mem c_buffer=clCreateBuffer(context,CL_MEM_READ_WRITE,sizeof(float)*4*4,NULL,&status);
status=clSetKernelArg(kernel,0,sizeof(cl_mem),&a_buffer);
status=clSetKernelArg(kernel,1,sizeof(cl_mem),&b_buffer);
status=clSetKernelArg(kernel,2,sizeof(cl_mem),&c_buffer);
status=clEnqueueWriteBuffer(queue,a_buffer,CL_TRUE,0,sizeof(float)*4*4,A,0,NULL,NULL);
printf("have written a\n");
status=clEnqueueWriteBuffer(queue,b_buffer,CL_TRUE,0,sizeof(float)*4*4,B,0,NULL,NULL);
printf("have written b\n");
size_t global_item_size = 4;
size_t local_item_size = 1;
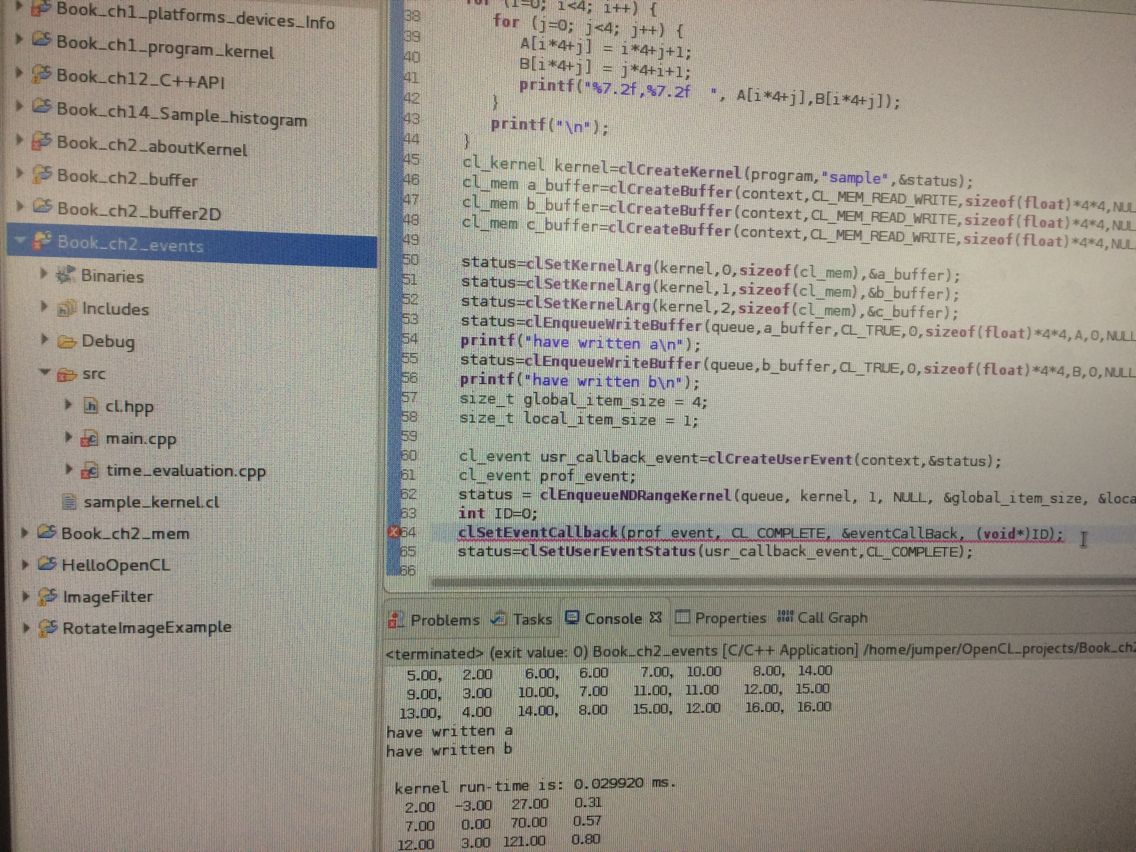
cl_event usr_callback_event=clCreateUserEvent(context,&status);
cl_event prof_event;
status = clEnqueueNDRangeKernel(queue, kernel, 1, NULL, &global_item_size, &local_item_size, 1, &usr_callback_event, &prof_event);
int ID=0;
clSetEventCallback(prof_event, CL_COMPLETE, &eventCallBack, (void*)ID);
status=clSetUserEventStatus(usr_callback_event,CL_COMPLETE);
status = clEnqueueReadBuffer(queue, c_buffer, CL_TRUE, 0, 4*4*sizeof(float), C, 0, NULL, NULL);
for (i=0; i<4; i++) {
for (j=0; j<4; j++) {
printf("%7.2f ", C[i*4+j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
clReleaseCommandQueue(queue);
clReleaseKernel(kernel);
clReleaseProgram(program);
clReleaseMemObject(a_buffer);
clReleaseMemObject(b_buffer);
clReleaseMemObject(c_buffer);
clReleaseContext(context);
clReleaseEvent(usr_callback_event);
clReleaseEvent(prof_event);
return 0;
}
但有个问题:之前我写过一个event的工程 先试卡在事件那里 后来我把seteventstatus放在执行commandqueue前面 就可以了 但这个程序中是放在后面的 为什么不卡呢??
status=clSetUserEventStatus(usr_callback_event,CL_COMPLETE);《OpenCL编程指南》我跨过了与3D渲染有关的:OpenCL、Direct3D的交互以及嵌入式。这些我暂时用不到。
《OpenCL编程指南》第二部分 案例研究
一、图像直方图计算
我开始自己写了个:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <CL/cl.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include "FreeImage.h"
#include "gFreeImage.h"
cl_mem LoadImage(cl_context context, char *fileName, int &width, int &height)
{
FREE_IMAGE_FORMAT format = FreeImage_GetFileType(fileName, 0);
FIBITMAP* image = FreeImage_Load(format, fileName);
// Convert to 32-bit image
FIBITMAP* temp = image;
image = FreeImage_ConvertTo32Bits(image);
FreeImage_Unload(temp);
width = FreeImage_GetWidth(image);
height = FreeImage_GetHeight(image);
char *buffer = new char[width * height * 4];
memcpy(buffer, FreeImage_GetBits(image), width * height * 4);
FreeImage_Unload(image);
// Create OpenCL image
cl_image_format clImageFormat;
clImageFormat.image_channel_order = CL_RGBA;
clImageFormat.image_channel_data_type = CL_UNORM_INT8;
cl_int errNum;
cl_mem clImage;
clImage = clCreateImage2D(context, CL_MEM_READ_ONLY | CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR,&clImageFormat,width,height, 0,buffer,&errNum);
if (errNum != CL_SUCCESS)
{
std::cerr << "Error creating CL image object" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
delete [] buffer;
return clImage;
}
int main(){
cl_uint platformNum;
cl_int status;
status=clGetPlatformIDs(0,NULL,&platformNum);
if(status!=CL_SUCCESS){
printf("cannot get platforms number.\n");
return -1;
}
cl_platform_id* platforms;
platforms=(cl_platform_id*)alloca(sizeof(cl_platform_id)*platformNum);
status=clGetPlatformIDs(platformNum,platforms,NULL);
if(status!=CL_SUCCESS){
printf("cannot get platforms addresses.\n");
return -1;
}
cl_platform_id platformInUse=platforms[0];
cl_device_id device;
clGetDeviceIDs(platformInUse,CL_DEVICE_TYPE_GPU,1,&device,NULL);
cl_context context=clCreateContext(NULL,1,&device,NULL,NULL,NULL);
cl_command_queue queue=clCreateCommandQueue(context,device,CL_QUEUE_PROFILING_ENABLE, &status);
//Create Input Image Object
char file[]={"/home/jumper/OpenCL_projects/Book_ch14_Sample_histogram/lenna.jpg"};
int imgwidth,imgheight;
cl_mem image=LoadImage(context,file,imgwidth,imgheight);
cl_sampler sampler=clCreateSampler(context,CL_FALSE, CL_ADDRESS_CLAMP_TO_EDGE,CL_FILTER_NEAREST,&status);
cl_mem outmem=clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_WRITE_ONLY,sizeof(int)*256*3,NULL,NULL);
std::ifstream srcFile("/home/jumper/OpenCL_projects/Book_ch14_Sample_histogram/histogramcl.cl");
std::string srcProg(std::istreambuf_iterator<char>(srcFile),(std::istreambuf_iterator<char>()));
const char * src = srcProg.c_str();
size_t length = srcProg.length();
cl_program program=clCreateProgramWithSource(context,1,&src,&length,&status);
status=clBuildProgram(program,1,&device,NULL,NULL,NULL);
cl_kernel kernel=clCreateKernel(program,"calculateHistogram",NULL);
status = clSetKernelArg(kernel, 0, sizeof(cl_mem), &image);
status |= clSetKernelArg(kernel, 1, sizeof(cl_mem), &outmem);
status |= clSetKernelArg(kernel, 2, sizeof(cl_sampler), &sampler);
status |= clSetKernelArg(kernel, 3, sizeof(cl_int), &imgwidth);
status |= clSetKernelArg(kernel, 4, sizeof(cl_int), &imgheight);
size_t localWorkSize[2] = { 16, 16 };
size_t globalWorkSize[2] = {imgwidth,imgheight};
clEnqueueNDRangeKernel(queue,kernel,2, NULL,globalWorkSize, localWorkSize,0, NULL, NULL);
int* outHistogram=(int*)alloca(sizeof(int)*256*3);
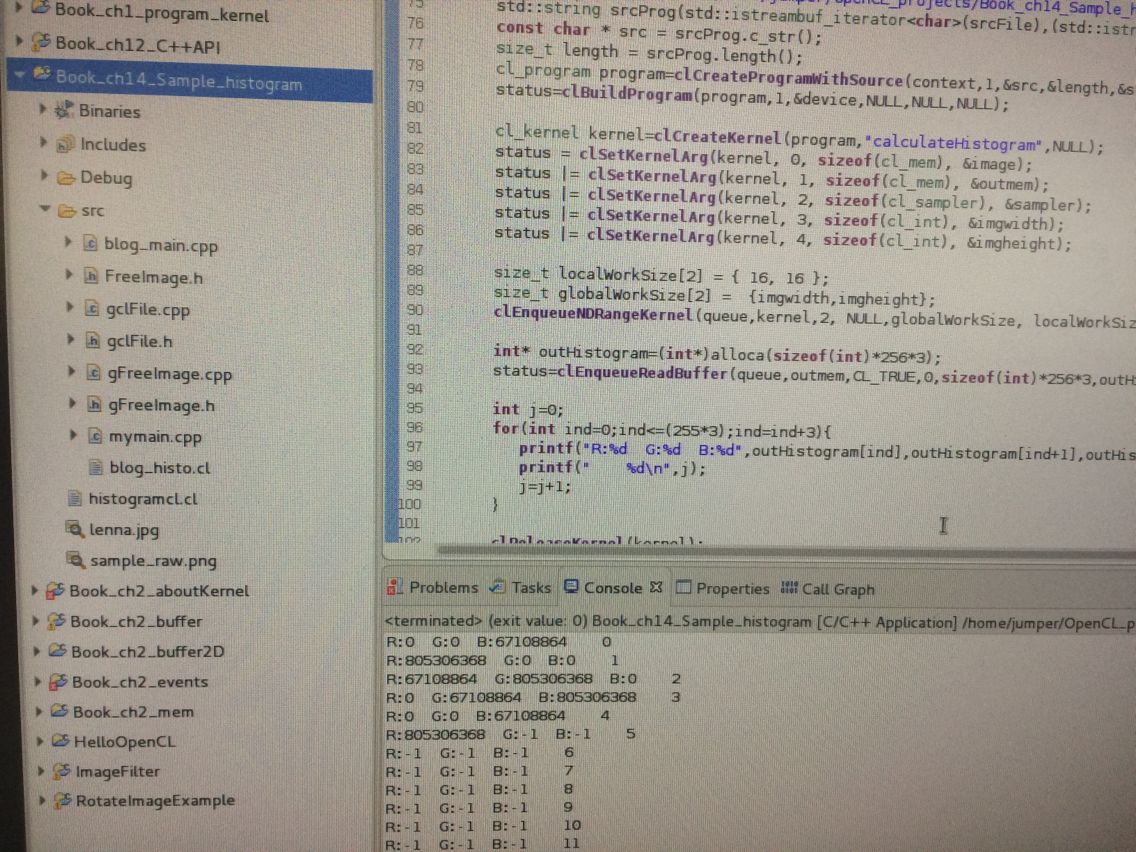
status=clEnqueueReadBuffer(queue,outmem,CL_TRUE,0,sizeof(int)*256*3,outHistogram,0,NULL,NULL);
int j=0;
for(int ind=0;ind<=(255*3);ind=ind+3){
printf("R:%d G:%d B:%d",outHistogram[ind],outHistogram[ind+1],outHistogram[ind+2]);
printf(" %d\n",j);
j=j+1;
}
clReleaseKernel(kernel);
clReleaseProgram(program);
clReleaseCommandQueue(queue);
clReleaseMemObject(image);
clReleaseMemObject(outmem);
clReleaseContext(context);
return 0;
}其中我的kernel是:
__kernel void calculateHistogram(__read_only image2d_t srcimg,__global const int *outmatrix,sample_t sampler,__global const int width,__global const int height){
int2 srcposition=(int2)(get_global_id(0),get_global_id(1));
if (srcposition.x < width && srcposition.y < height)
{
int4 positionValue = (int4)(0, 0, 0, 0);
positionValue = read_imagef(srcImg, sampler, (int2)(x, y)) ;
int RValue=position.x;
int GValue=position.y;
int BValue=position.z;
outmatrix[RValue*2+RValue]=outmatrix[RValue*2+RValue]+1;
outmatrix[GValue*3+GValue]=outmatrix[GValue*3+GValue]+1;
outmatrix[BValue*4+BValue]=outmatrix[BValue*4+BValue]+1;
}
}但结果出来不对 又出现这种无意义的数:
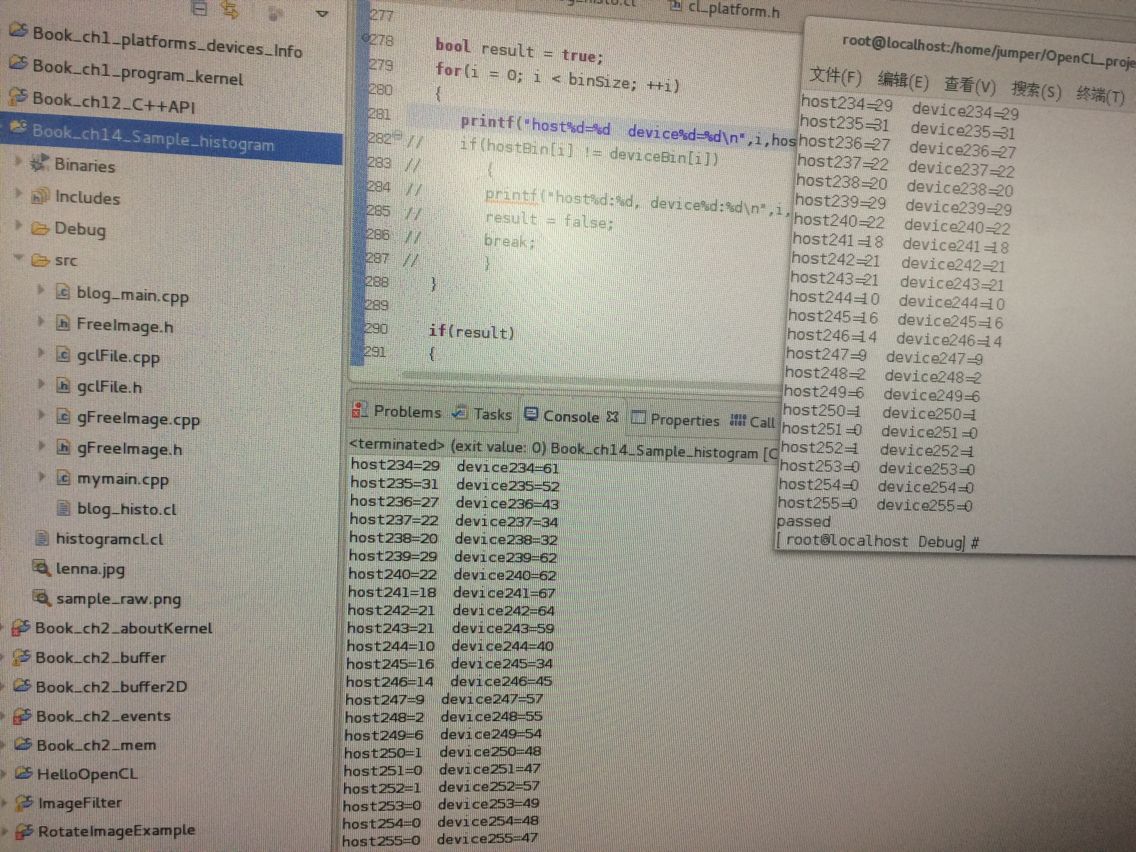
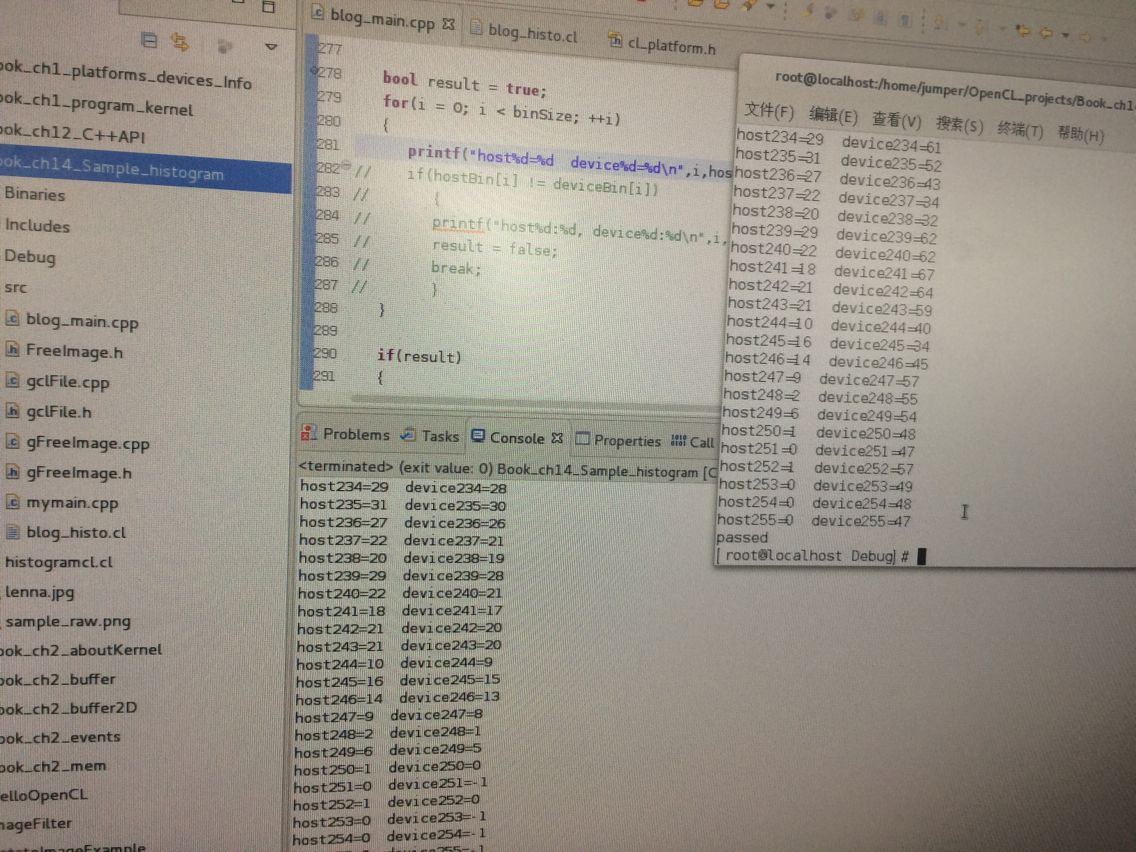
对于这种无意义的数 应该是和前几次我出现无意义的数一样的问题 只是我没找到而已 ???????
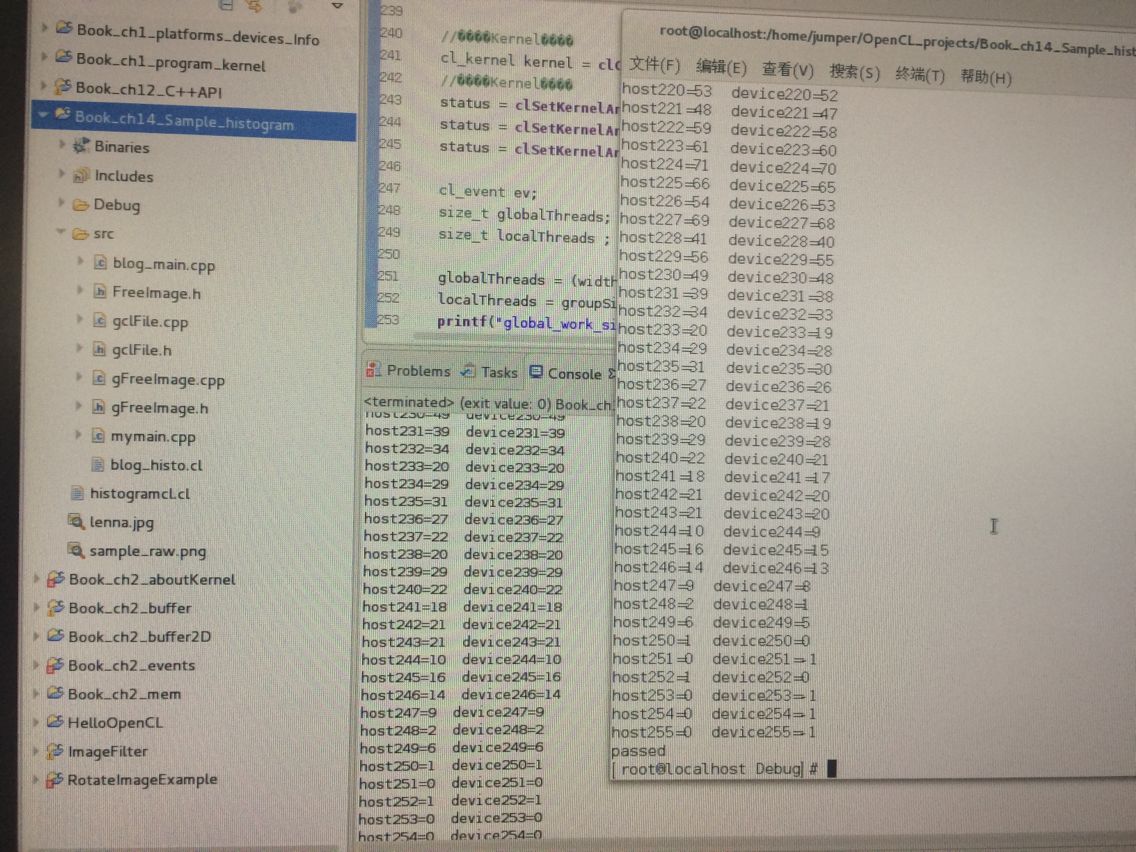
还有我看了博客http://www.cnblogs.com/mikewolf2002/archive/2012/10/22/2734462.html 大神的计算直方图 出来好奇怪:
#include <CL/cl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string.h>
#include "gclFile.h"
#include "gFreeImage.h"
using namespace std;
//#pragma comment (lib,"OpenCL.lib")
//#pragma comment(lib,"freeimage.lib")
cl_int binSize; //bins�Ĵ�С�����ڻҶ�ͼ��һ��Ϊ256
cl_int groupSize; //workgroup��С
cl_int subHistgCnt; //��ͼ��ֿ�����ֱ��ͼ������ٺϲ�������ͼ���ֱ��ͼ
cl_uint *data; //ͼ������
cl_int width; //ͼ����
cl_int height; //ͼ��߶�
cl_uint *hostBin; //cpu����õ�������ֱ��ͼ���
cl_uint *midDeviceBin; //gpu�����ӿ��ֱ��ͼ�����Ҳ��kernel����Ľ�����ϲ���deviceBin�С�
cl_uint *deviceBin; //�豸(gpu)���������ս��
cl_mem dataBuf; //ͼ��device memory
cl_mem midDeviceBinBuf; //�ӿ�ֱ��ͼ���device memory���������������һ��������kernel������
//cpu��ֱ��ͼ
void cpu_histgo()
{
int i, j;
for(i = 0; i < height; ++i)
{
for(j = 0; j < width; ++j)
{
//printf("data: %d\n", data[i * width + j] );
hostBin[data[i * width + j]]++;
//printf("hostbin %d=%d\n", data[i * width + j], hostBin[data[i * width + j]]);
}
}
}
int waitForEventAndRelease(cl_event *event)
{
cl_int status = CL_SUCCESS;
cl_int eventStatus = CL_QUEUED;
while(eventStatus != CL_COMPLETE)
{
status = clGetEventInfo(
*event,
CL_EVENT_COMMAND_EXECUTION_STATUS,
sizeof(cl_int),
&eventStatus,
NULL);
}
status = clReleaseEvent(*event);
return 0;
}
int main0(int argc, char* argv[])
{
unsigned char *src_image=0;
gFreeImage img;
if(!img.LoadImageGrey("/home/jumper/OpenCL_projects/Book_ch14_Sample_histogram/sample_raw.png"))
{
printf("can not load lenna.jpg\n");
exit(0);
}
src_image = img.getImageDataGrey(width,height);
binSize = 256;
groupSize = 128;
subHistgCnt = (width *height)/(binSize * groupSize);
//width��binSize����������height��groupsize��������
width = (width / binSize ? width / binSize: 1) * binSize;
height = (height / groupSize ? height / groupSize: 1) * groupSize;
// ����ͼ������
data = (cl_uint*)malloc(width * height * sizeof(cl_uint));
if(!data)
{
printf("malloc error\n");
return 0;
}
memset(data, 0,width * height * sizeof(cl_uint));
int i, j;
//��ÿ������ֵ����һ��float���飬��Ҫ�Ǽ��㷽�㣬Ҳ������kernel��ֱ����uchar
for(i = 0; i < width * height; i++)
{
data[i] = (cl_uint)src_image[i];
//printf("%d\n", data[i]);
//printf("src= %d\n", src_image[i]);
}
hostBin = (cl_uint*)malloc(binSize * sizeof(cl_uint));
if(!hostBin)
{
printf("malloc error\n");
return 0;
}
memset(hostBin, 0, binSize * sizeof(cl_uint));
midDeviceBin = (cl_uint*)malloc(binSize * subHistgCnt * sizeof(cl_uint));
if(!midDeviceBin)
{
printf("malloc error\n");
return 0;
}
memset(midDeviceBin, 0, binSize * subHistgCnt * sizeof(cl_uint));
deviceBin = (cl_uint*)malloc(binSize * sizeof(cl_uint));
if(!deviceBin)
{
printf("malloc error\n");
return 0;
}
memset(deviceBin, 0, binSize * sizeof(cl_uint));
//����driver dump il��isa�ļ�
//_putenv("GPU_DUMP_DEVICE_KERNEL=3");
cl_uint status;
cl_platform_id platform;
//����ƽ̨����
//status = clGetPlatformIDs( 1, &platform, NULL );
cl_uint numPlatforms;
std::string platformVendor;
status = clGetPlatformIDs(0, NULL, &numPlatforms);
if(status != CL_SUCCESS)
{
return 0;
}
if (0 < numPlatforms)
{
cl_platform_id* platforms = new cl_platform_id[numPlatforms];
status = clGetPlatformIDs(numPlatforms, platforms, NULL);
char platformName[100];
for (unsigned i = 0; i < numPlatforms; ++i)
{
status = clGetPlatformInfo(platforms[i],
CL_PLATFORM_VENDOR,
sizeof(platformName),
platformName,
NULL);
platform = platforms[i];
platformVendor.assign(platformName);
if (!strcmp(platformName, "Advanced Micro Devices, Inc."))
{
break;
}
}
std::cout << "Platform found : " << platformName << "\n";
delete[] platforms;
}
cl_device_id device;
//����GPU�豸
clGetDeviceIDs( platform, CL_DEVICE_TYPE_GPU,
1,
&device,
NULL);
//����context
cl_context context = clCreateContext( NULL,
1,
&device,
NULL, NULL, NULL);
//�����������
cl_command_queue queue = clCreateCommandQueue( context,
device,
CL_QUEUE_PROFILING_ENABLE, NULL );
//����2��OpenCL�ڴ����
dataBuf = clCreateBuffer(
context,
CL_MEM_READ_ONLY,
sizeof(cl_uint) * width * height,
NULL,
0);
midDeviceBinBuf = clCreateBuffer(
context,
CL_MEM_WRITE_ONLY,
sizeof(cl_uint) * binSize * subHistgCnt,
NULL,
0);
//��ͼ������д��device memory��
cl_event writeEvt;
status = clEnqueueWriteBuffer(queue,
dataBuf,
CL_FALSE,
0,
width * height * sizeof(cl_uint),
data,
0,
NULL,
&writeEvt);
status = clFlush(queue);
waitForEventAndRelease(&writeEvt);
//kernel�ļ�Ϊhisto.cl
gclFile kernelFile;
if(!kernelFile.open("/home/jumper/OpenCL_projects/Book_ch14_Sample_histogram/src/blog_histo.cl"))
{
printf("Failed to load kernel file \n");
exit(0);
}
const char * source = kernelFile.source().c_str();
size_t sourceSize[] = {strlen(source)};
//�����������
cl_program program = clCreateProgramWithSource(context, 1, &source,sourceSize,NULL);
//����������
status = clBuildProgram( program, 1, &device, NULL, NULL, NULL );
if(status != 0)
{
printf("clBuild failed:%d\n", status);
char tbuf[0x10000];
clGetProgramBuildInfo(program, device, CL_PROGRAM_BUILD_LOG, 0x10000, tbuf, NULL);
printf("\n%s\n", tbuf);
return -1;
}
//����Kernel����
cl_kernel kernel = clCreateKernel( program, "histogram256", NULL );
//����Kernel����
cl_mem pos=clCreateBuffer( context,CL_MEM_WRITE_ONLY,groupSize * binSize * sizeof(cl_uchar),NULL,0);
status = clSetKernelArg(kernel, 0, sizeof(cl_mem), (void*)&dataBuf);
status = clSetKernelArg(kernel, 1, groupSize * binSize * sizeof(cl_uchar), NULL); //local memroy size, lds for amd
status = clSetKernelArg(kernel, 2, sizeof(cl_mem), (void*)&midDeviceBinBuf);
cl_event ev;
size_t globalThreads;
size_t localThreads ;
globalThreads = (width * height) / binSize ;
localThreads = groupSize;
printf("global_work_size =%d, local_work_size=%d\n", globalThreads, localThreads);
clEnqueueNDRangeKernel( queue,kernel,1,NULL,&globalThreads,&localThreads, 0, NULL, &ev);
clFlush( queue );
waitForEventAndRelease(&ev);
// cl_ulong startTime, endTime;
// clGetEventProfilingInfo(ev, CL_PROFILING_COMMAND_START, sizeof(cl_ulong), &startTime, NULL); //error accured when run this code sentence!???????
// clGetEventProfilingInfo(ev, CL_PROFILING_COMMAND_END,sizeof(cl_ulong), &endTime, NULL);
// cl_ulong kernelExecTimeNs = endTime-startTime;
// printf("kernal exec time :%8.6f ms\n ", kernelExecTimeNs*1e-6 );
cl_event readEvt;
status = clEnqueueReadBuffer(queue, midDeviceBinBuf, CL_FALSE,0,subHistgCnt * binSize * sizeof(cl_uint),midDeviceBin,0,NULL,&readEvt);
clWaitForEvents(1, &readEvt);
for(i = 0; i < subHistgCnt; ++i)
{
for( j = 0; j < binSize; ++j)
{
deviceBin[j] += midDeviceBin[i * binSize + j];
}
}
cpu_histgo();
bool result = true;
for(i = 0; i < binSize; ++i)
{
printf("host%d=%d device%d=%d\n",i,hostBin[i], i, deviceBin[i]);
// if(hostBin[i] != deviceBin[i])
// {
// printf("host%d:%d, device%d:%d\n",i, hostBin[i], i, deviceBin[i]);
// result = false;
// break;
// }
}
if(result)
{
printf("passed\n");
}
else
{
printf("failed\n");
}
free(data);
free(hostBin);
free(midDeviceBin);
free(deviceBin);
//ɾ��OpenCL��Դ����
clReleaseProgram(program);
clReleaseCommandQueue(queue);
clReleaseContext(context);
return 0;
}#define LINEAR_MEM_ACCESS
#pragma OPENCL EXTENSION cl_khr_byte_addressable_store : enable
#define BIN_SIZE 256
__kernel void histogram256(__global const uint* data,__local uchar* sharedArray,__global uint* binResult)
{
size_t localId = get_local_id(0);
size_t globalId = get_global_id(0);
size_t groupId = get_group_id(0);
size_t groupSize = get_local_size(0);
for(int i = 0; i < BIN_SIZE; ++i)
sharedArray[localId * BIN_SIZE + i] = 0;
barrier(CLK_LOCAL_MEM_FENCE);
for(int i = 0; i < BIN_SIZE; ++i)
{
#ifdef LINEAR_MEM_ACCESS
uint value = data[groupId * groupSize * BIN_SIZE + i * groupSize + localId];
#else
uint value = data[globalId * BIN_SIZE + i];
#endif // LINEAR_MEM_ACCESS
sharedArray[localId * BIN_SIZE + value]++;
}
barrier(CLK_LOCAL_MEM_FENCE);
for(int i = 0; i < BIN_SIZE / groupSize; ++i)
{
uint binCount = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < groupSize; ++j)
binCount += sharedArray[j * BIN_SIZE + i * groupSize + localId];
binResult[groupId * BIN_SIZE + i * groupSize + localId] = binCount;
}
}
看一会儿正确一会儿不正确!???!!!不管是用终端还是用eclipse 我没改动过 同样的工程和图片 我和同事看了下发现第二个参数他传的NULL进来,同事说可能这里的问题导致的?:
status = clSetKernelArg(kernel, 1, groupSize * binSize * sizeof(cl_uchar), NULL);
智能推荐
攻防世界_难度8_happy_puzzle_攻防世界困难模式攻略图文-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读645次。这个肯定是末尾的IDAT了,因为IDAT必须要满了才会开始一下个IDAT,这个明显就是末尾的IDAT了。,对应下面的create_head()代码。,对应下面的create_tail()代码。不要考虑爆破,我已经试了一下,太多情况了。题目来源:UNCTF。_攻防世界困难模式攻略图文
达梦数据库的导出(备份)、导入_达梦数据库导入导出-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读2.9k次,点赞3次,收藏10次。偶尔会用到,记录、分享。1. 数据库导出1.1 切换到dmdba用户su - dmdba1.2 进入达梦数据库安装路径的bin目录,执行导库操作 导出语句:./dexp cwy_init/[email protected]:5236 file=cwy_init.dmp log=cwy_init_exp.log 注释: cwy_init/init_123..._达梦数据库导入导出
js引入kindeditor富文本编辑器的使用_kindeditor.js-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1.9k次。1. 在官网上下载KindEditor文件,可以删掉不需要要到的jsp,asp,asp.net和php文件夹。接着把文件夹放到项目文件目录下。2. 修改html文件,在页面引入js文件:<script type="text/javascript" src="./kindeditor/kindeditor-all.js"></script><script type="text/javascript" src="./kindeditor/lang/zh-CN.js"_kindeditor.js
STM32学习过程记录11——基于STM32G431CBU6硬件SPI+DMA的高效WS2812B控制方法-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读2.3k次,点赞6次,收藏14次。SPI的详情简介不必赘述。假设我们通过SPI发送0xAA,我们的数据线就会变为10101010,通过修改不同的内容,即可修改SPI中0和1的持续时间。比如0xF0即为前半周期为高电平,后半周期为低电平的状态。在SPI的通信模式中,CPHA配置会影响该实验,下图展示了不同采样位置的SPI时序图[1]。CPOL = 0,CPHA = 1:CLK空闲状态 = 低电平,数据在下降沿采样,并在上升沿移出CPOL = 0,CPHA = 0:CLK空闲状态 = 低电平,数据在上升沿采样,并在下降沿移出。_stm32g431cbu6
计算机网络-数据链路层_接收方收到链路层数据后,使用crc检验后,余数为0,说明链路层的传输时可靠传输-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1.2k次,点赞2次,收藏8次。数据链路层习题自测问题1.数据链路(即逻辑链路)与链路(即物理链路)有何区别?“电路接通了”与”数据链路接通了”的区别何在?2.数据链路层中的链路控制包括哪些功能?试讨论数据链路层做成可靠的链路层有哪些优点和缺点。3.网络适配器的作用是什么?网络适配器工作在哪一层?4.数据链路层的三个基本问题(帧定界、透明传输和差错检测)为什么都必须加以解决?5.如果在数据链路层不进行帧定界,会发生什么问题?6.PPP协议的主要特点是什么?为什么PPP不使用帧的编号?PPP适用于什么情况?为什么PPP协议不_接收方收到链路层数据后,使用crc检验后,余数为0,说明链路层的传输时可靠传输
软件测试工程师移民加拿大_无证移民,未受过软件工程师的教育(第1部分)-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读587次。软件测试工程师移民加拿大 无证移民,未受过软件工程师的教育(第1部分) (Undocumented Immigrant With No Education to Software Engineer(Part 1))Before I start, I want you to please bear with me on the way I write, I have very little gen...
随便推点
Thinkpad X250 secure boot failed 启动失败问题解决_安装完系统提示secureboot failure-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读304次。Thinkpad X250笔记本电脑,装的是FreeBSD,进入BIOS修改虚拟化配置(其后可能是误设置了安全开机),保存退出后系统无法启动,显示:secure boot failed ,把自己惊出一身冷汗,因为这台笔记本刚好还没开始做备份.....根据错误提示,到bios里面去找相关配置,在Security里面找到了Secure Boot选项,发现果然被设置为Enabled,将其修改为Disabled ,再开机,终于正常启动了。_安装完系统提示secureboot failure
C++如何做字符串分割(5种方法)_c++ 字符串分割-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读10w+次,点赞93次,收藏352次。1、用strtok函数进行字符串分割原型: char *strtok(char *str, const char *delim);功能:分解字符串为一组字符串。参数说明:str为要分解的字符串,delim为分隔符字符串。返回值:从str开头开始的一个个被分割的串。当没有被分割的串时则返回NULL。其它:strtok函数线程不安全,可以使用strtok_r替代。示例://借助strtok实现split#include <string.h>#include <stdio.h&_c++ 字符串分割
2013第四届蓝桥杯 C/C++本科A组 真题答案解析_2013年第四届c a组蓝桥杯省赛真题解答-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读2.3k次。1 .高斯日记 大数学家高斯有个好习惯:无论如何都要记日记。他的日记有个与众不同的地方,他从不注明年月日,而是用一个整数代替,比如:4210后来人们知道,那个整数就是日期,它表示那一天是高斯出生后的第几天。这或许也是个好习惯,它时时刻刻提醒着主人:日子又过去一天,还有多少时光可以用于浪费呢?高斯出生于:1777年4月30日。在高斯发现的一个重要定理的日记_2013年第四届c a组蓝桥杯省赛真题解答
基于供需算法优化的核极限学习机(KELM)分类算法-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读851次,点赞17次,收藏22次。摘要:本文利用供需算法对核极限学习机(KELM)进行优化,并用于分类。
metasploitable2渗透测试_metasploitable2怎么进入-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1.1k次。一、系统弱密码登录1、在kali上执行命令行telnet 192.168.26.1292、Login和password都输入msfadmin3、登录成功,进入系统4、测试如下:二、MySQL弱密码登录:1、在kali上执行mysql –h 192.168.26.129 –u root2、登录成功,进入MySQL系统3、测试效果:三、PostgreSQL弱密码登录1、在Kali上执行psql -h 192.168.26.129 –U post..._metasploitable2怎么进入
Python学习之路:从入门到精通的指南_python人工智能开发从入门到精通pdf-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读257次。本文将为初学者提供Python学习的详细指南,从Python的历史、基础语法和数据类型到面向对象编程、模块和库的使用。通过本文,您将能够掌握Python编程的核心概念,为今后的编程学习和实践打下坚实基础。_python人工智能开发从入门到精通pdf